Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Load and Plot from a File#
Read a dataset from a known file type.
Loading a mesh is trivial - if your data is in one of the many supported
file formats, simply use pyvista.read() to load your spatially
referenced dataset into a PyVista mesh object.
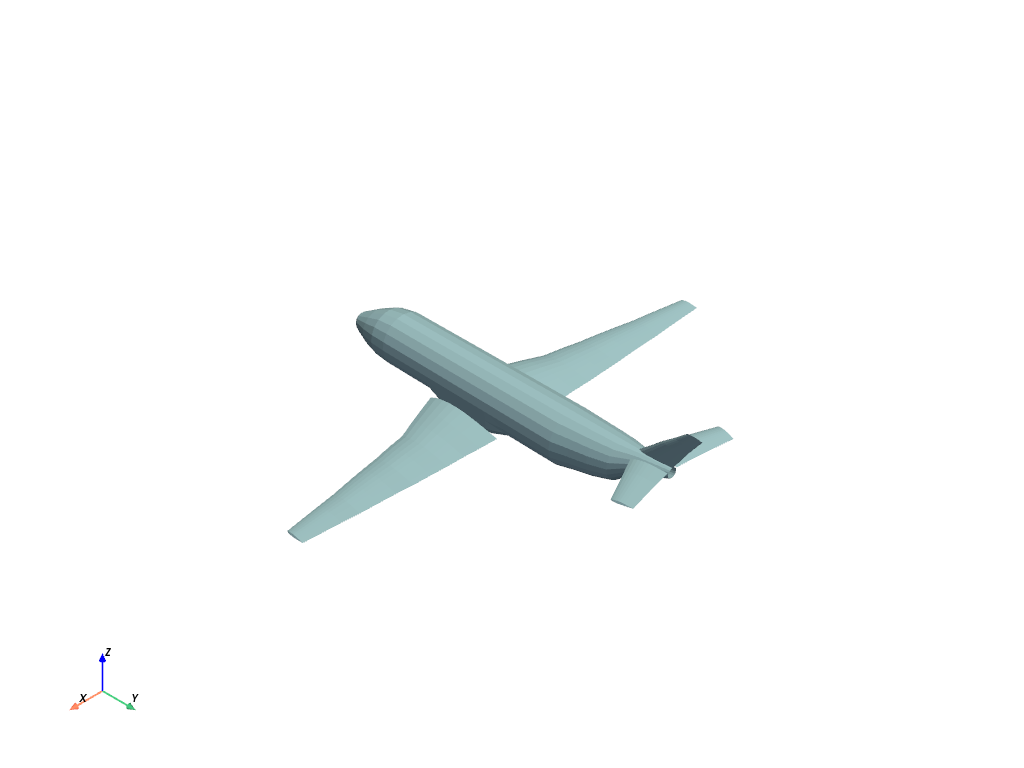
The following code block uses a built-in example file and displays an airplane mesh.
from __future__ import annotations
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
The following code block uses a built-in example file, displays an airplane mesh and returns the camera’s position:
# Get a sample file
filename = examples.planefile
filename
'/home/runner/work/pyvista/pyvista/pyvista/examples/airplane.ply'
Note the above filename, it’s a .ply file - one of the many supported
formats in PyVista.

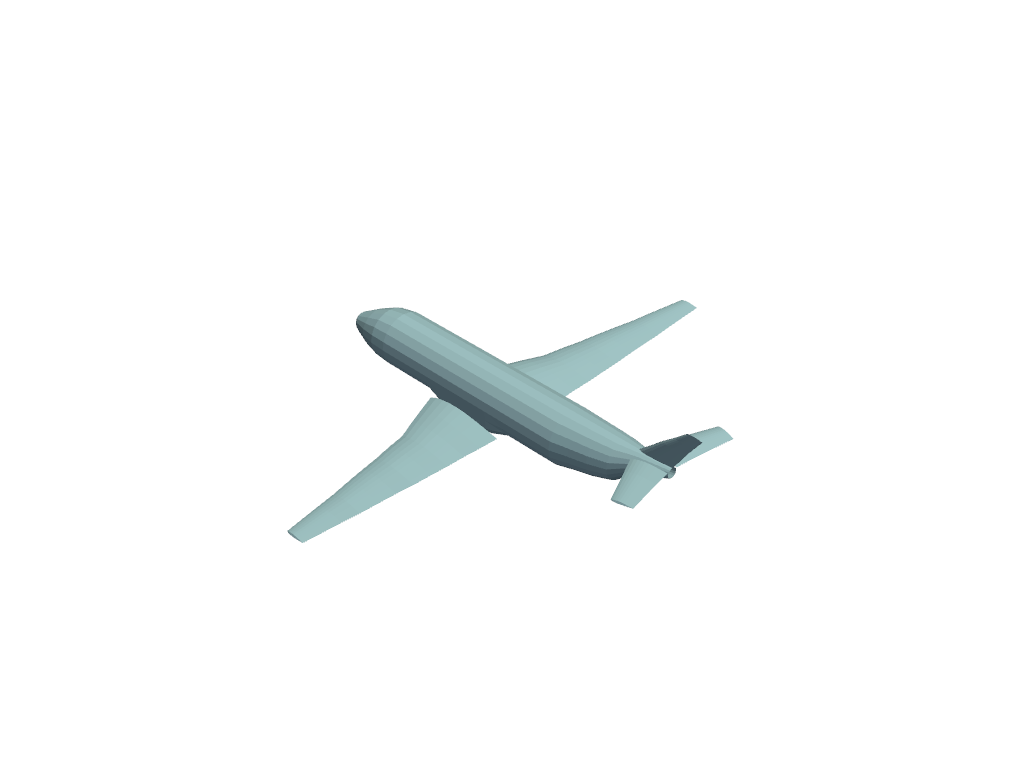
You can also take a screenshot without creating an interactive plot window
using the Plotter:
plotter = pv.Plotter(off_screen=True)
plotter.add_mesh(mesh)
plotter.show(screenshot="myscreenshot.png")

The points from the mesh are directly accessible as a NumPy array:
mesh.points
pyvista_ndarray([[896.994 , 48.7601 , 82.2656 ],
[906.593 , 48.7601 , 80.7452 ],
[907.539 , 55.4902 , 83.6581 ],
...,
[806.665 , 627.363 , 5.11482],
[806.665 , 654.432 , 7.51998],
[806.665 , 681.537 , 9.48744]], dtype=float32)
The faces from the mesh are also directly accessible as a NumPy array:
mesh.faces.reshape(-1, 4)[:, 1:] # triangular faces
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 0, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 1],
...,
[1324, 1333, 1323],
[1325, 1216, 1334],
[1325, 1334, 1324]])
Loading other files types is just as easy. Simply pass your file path to the
pyvista.read() function and that’s it.
Here are a few other examples - simply replace examples.download_* in the
examples below with pyvista.read('path/to/you/file.ext')
Example STL file:
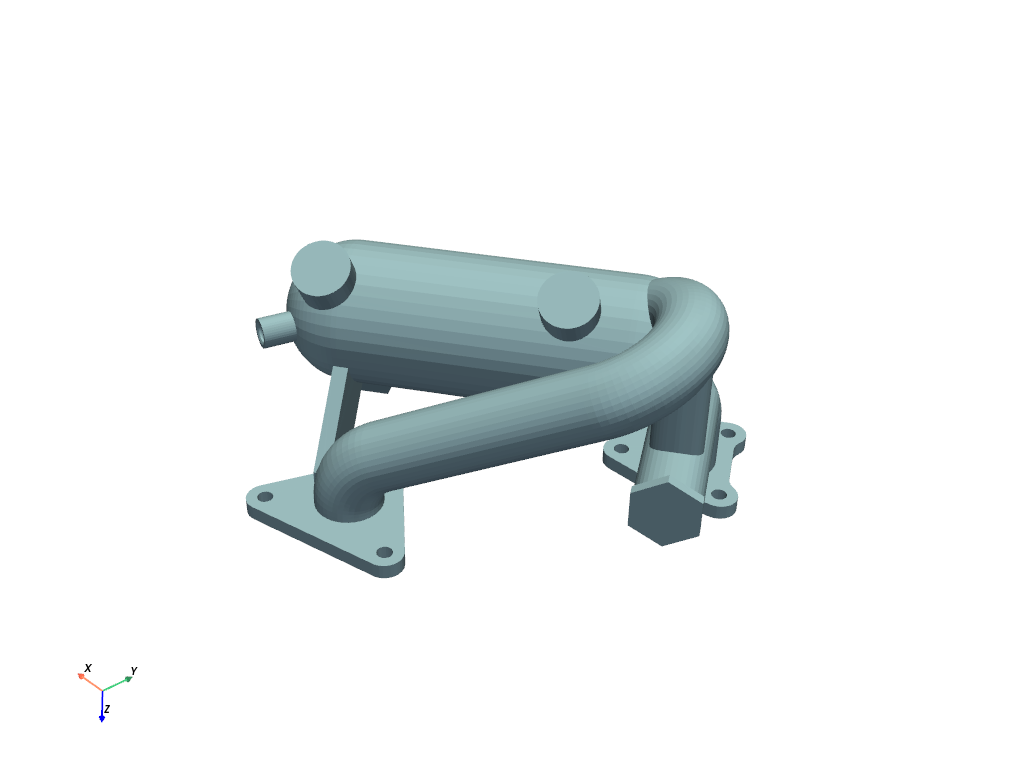

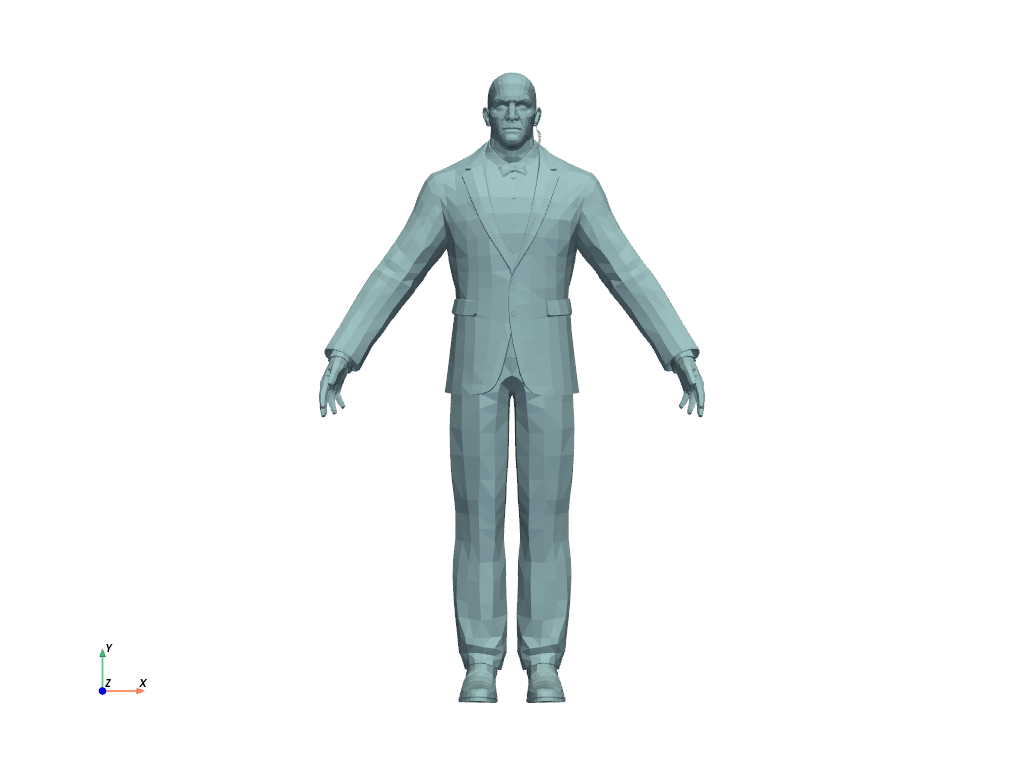
Example OBJ file
mesh = examples.download_doorman()
mesh.plot(cpos="xy")
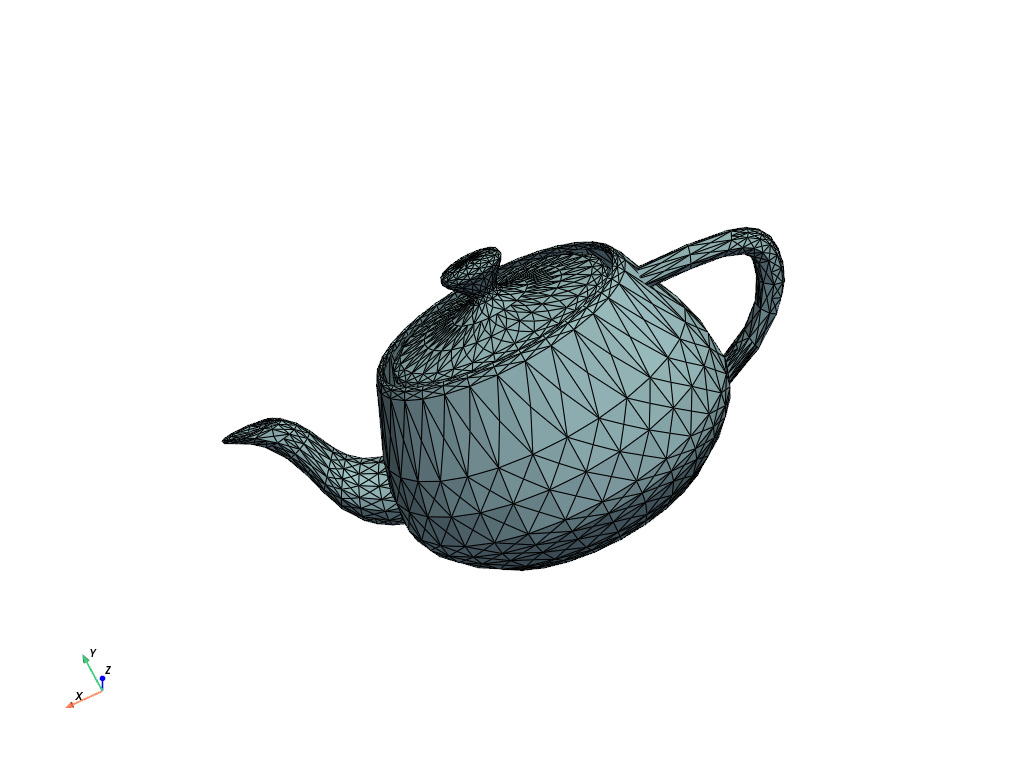
Example BYU file
mesh = examples.download_teapot()
mesh.plot(cpos=[-1, 2, -5], show_edges=True)

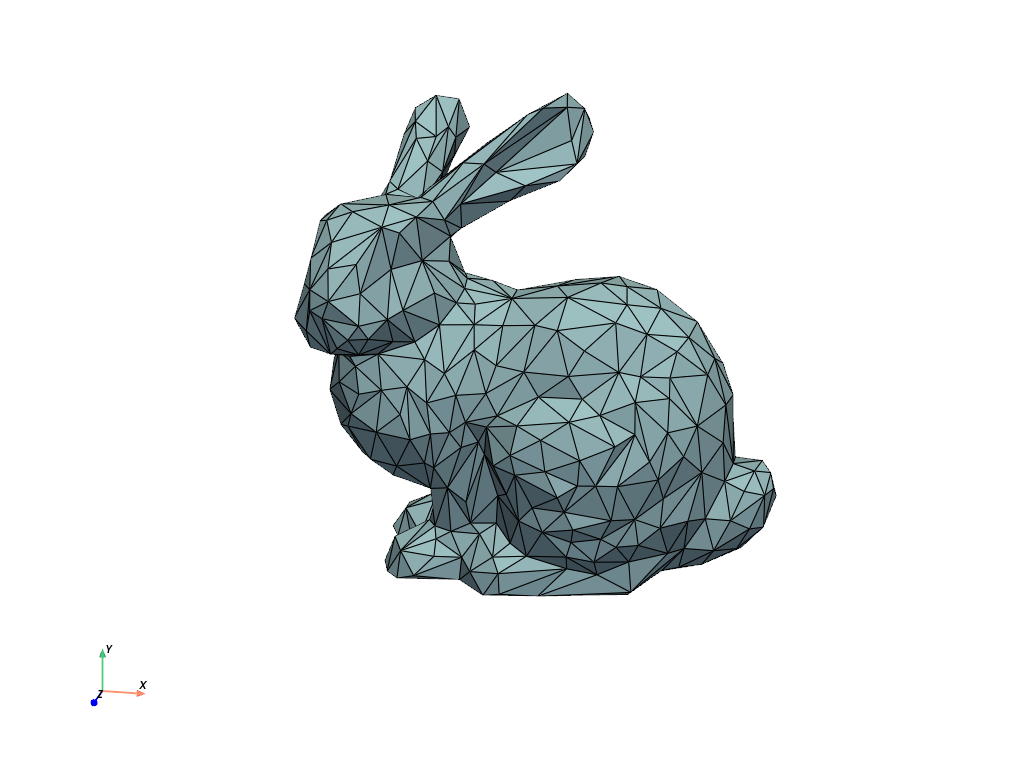
Example VTK file
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.443 seconds)
