pyvista.PolyData#
- class PolyData(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
Dataset consisting of surface geometry (e.g. vertices, lines, and polygons).
The surface geometry is defined by its
pointsand four separate cell connectivity arrays:vertsfor 0-dimensionalVERTEXandPOLY_VERTEXcells.stripsfor 2-dimensionalTRIANGLE_STRIPcells.
Cell types can be mixed, and any combination of cell connectivity array(s) may be specified.
PolyDatacan be initialized in several ways:Create an empty mesh
Initialize from a vtkPolyData
Using points only
Using points with verts, faces, lines, and/or strips
From a file
If a points array is provided with no cell connectivity, the
vertsconnectivity is populated by default, and each point is automatically associated with a singleVERTEXto create a point cloud wheren_vertsequalsn_points.Deprecated since version 0.44.0: The parameters
n_faces,n_lines,n_strips, andn_vertsare deprecated and no longer used. They were previously used to speed up the construction of the corresponding cell arrays but no longer provide any benefit.- Parameters:
- var_inpvtkPolyData,
str, sequence,optional Flexible input type. Can be a vtkPolyData, in which case this PolyData object will be copied if
deep=Trueand will be a shallow copy ifdeep=False.Also accepts a path, which may be local path as in
'my_mesh.stl'or global path like'/tmp/my_mesh.ply'or'C:/Users/user/my_mesh.ply'.Otherwise, this must be a points array or list containing one or more points. Each point must have 3 dimensions. If
faces,lines,strips, andvertsare allNone, then thePolyDataobject will be created with vertex cells withn_vertsequal to the number ofpoints.- faces
CellArrayLike,optional Connectivity of polygonal
faces. Can be either a padded connectivity array or an explicit cell array object.In the padded array format, faces must contain padding indicating the number of points in the face. For example, the two faces
[10, 11, 12]and[20, 21, 22, 23]will be represented as[3, 10, 11, 12, 4, 20, 21, 22, 23]. This lets you have an arbitrary number of points per face.- n_faces
int,optional Deprecated. Not used.
- lines
CellArrayLike,optional Connectivity of
lines. Likefaces, this can be either a padded connectivity array or an explicit cell array object. The padded array format requires padding indicating the number of points in a line segment. For example, the two line segments[0, 1]and[1, 2, 3, 4]will be represented as[2, 0, 1, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4].- n_lines
int,optional Deprecated. Not used.
- strips
CellArrayLikeoptional Connectivity of triangle
strips. Triangle strips require an initial triangle, and the following points of the strip. Each triangle is built with the new point and the two previous points.Just as in
linesandfaces, this connectivity can be specified as either a padded array or an explicit cell array object. The padded array requires a padding indicating the number of points. For example, a single triangle strip of the 10 point indices[0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 4, 5, 0, 1]requires padding of10and should be input as[10, 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 4, 5, 0, 1].- n_strips
int,optional Deprecated. Not used.
- deepbool,
optional Whether to copy the inputs, or to create a mesh from them without copying them. Setting
deep=Trueensures that the original arrays can be modified outside the mesh without affecting the mesh. Default isFalse.- force_ext
str,optional If initializing from a file, force the reader to treat the file as if it had this extension as opposed to the one in the file.
- force_floatbool,
optional Casts the datatype to
float32if points datatype is non-float. DefaultTrue. Set this toFalseto allow non-float types, though this may lead to truncation of intermediate floats when transforming datasets.- verts
CellArrayLike,optional The
vertsconnectivity. Likefaces,lines, andstripsthis can be supplied as either a padded array or an explicit cell array object. In the padded array format, the padding indicates the number of vertices in each cell. For example,[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2]indicates three vertex cells each with one point, and[2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 3]indicates two polyvertex cells each with two points.- n_verts
int,optional Deprecated. Not used.
- validatebool |
str| sequence[str], default:False Validate the mesh using
validate_mesh()after initialization. Set this toTrueto validate all fields, or specify any combination of fields allowed byvalidate_mesh.Added in version 0.47.
- var_inpvtkPolyData,
Examples
>>> import vtk >>> import numpy as np >>> from pyvista import examples >>> import pyvista as pv
Seed random number generator for reproducible plots
>>> rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)
Create an empty mesh.
>>> mesh = pv.PolyData()
Initialize from a vtkPolyData object.
>>> vtkobj = vtk.vtkPolyData() >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(vtkobj)
Initialize from just points, creating vertices
>>> points = np.array([[0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], [1, 0.5, 0], [0, 0.5, 0]]) >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(points)
Initialize from points and faces, creating polygonal faces.
>>> faces = np.hstack([[3, 0, 1, 2], [3, 0, 3, 2]]) >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(points, faces)
Initialize from points and lines.
>>> lines = np.hstack([[2, 0, 1], [2, 1, 2]]) >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(points, lines=lines)
Initialize from points and triangle strips.
>>> strips = np.hstack([[4, 0, 1, 3, 2]]) >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(points, strips=strips)
It is also possible to create with multiple cell types.
>>> verts = [1, 0] >>> lines = [2, 1, 2] >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(points, verts=verts, lines=lines)
Initialize from a filename.
>>> mesh = pv.PolyData(examples.antfile)
Construct a set of random line segments using a
pv.CellArray. Because every line in this example has the same size, in this case two points, we can usepv.CellArray.from_regular_cellsto construct thelinescell array. This is the most efficient method to construct a cell array.>>> n_points = 20 >>> n_lines = n_points // 2 >>> points = rng.random((n_points, 3)) >>> lines = rng.integers(low=0, high=n_points, size=(n_lines, 2)) >>> mesh = pv.PolyData(points, lines=pv.CellArray.from_regular_cells(lines)) >>> mesh.cell_data['line_idx'] = np.arange(n_lines) >>> mesh.plot(scalars='line_idx')
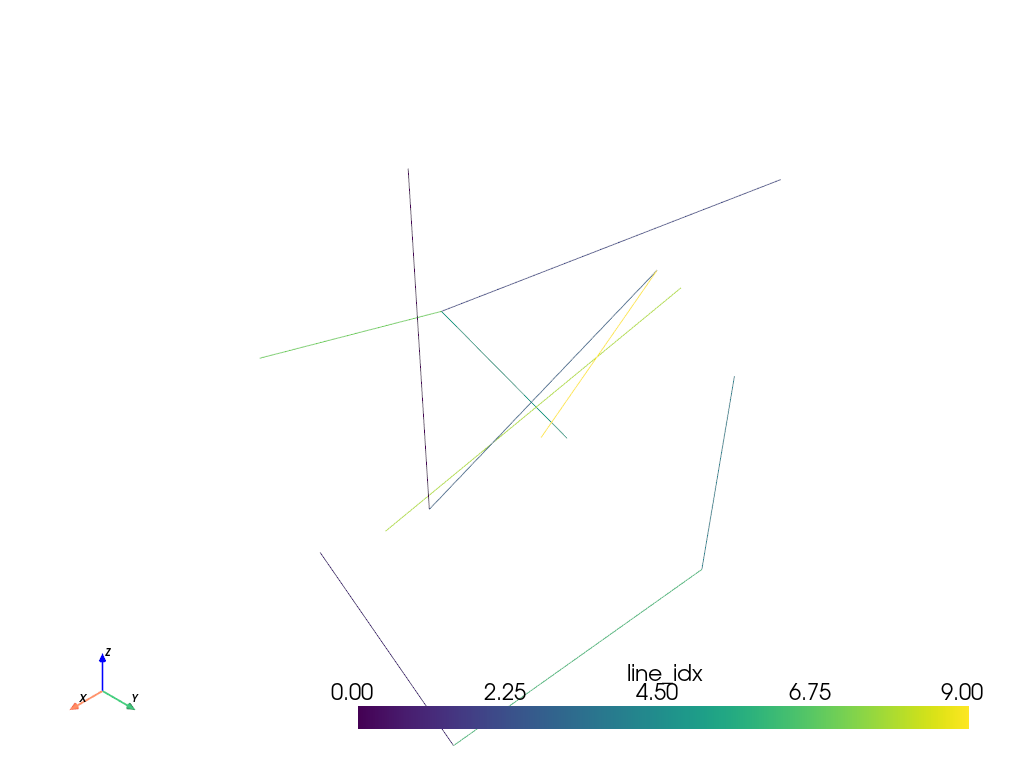
Construct a set of random triangle strips using a
pv.CellArray. Because each strip in this example can have a different number of points, we usepv.CellArray.from_irregular_cellsto construct thestripscell array.>>> n_strips = 4 >>> n_verts_per_strip = rng.integers(low=3, high=7, size=n_strips) >>> n_points = 10 * sum(n_verts_per_strip) >>> points = rng.random((n_points, 3)) >>> strips = [ ... rng.integers(low=0, high=n_points, size=nv) for nv in n_verts_per_strip ... ] >>> mesh = pv.PolyData( ... points, strips=pv.CellArray.from_irregular_cells(strips) ... ) >>> mesh.cell_data['strip_idx'] = np.arange(n_strips) >>> mesh.plot(show_edges=True, scalars='strip_idx')
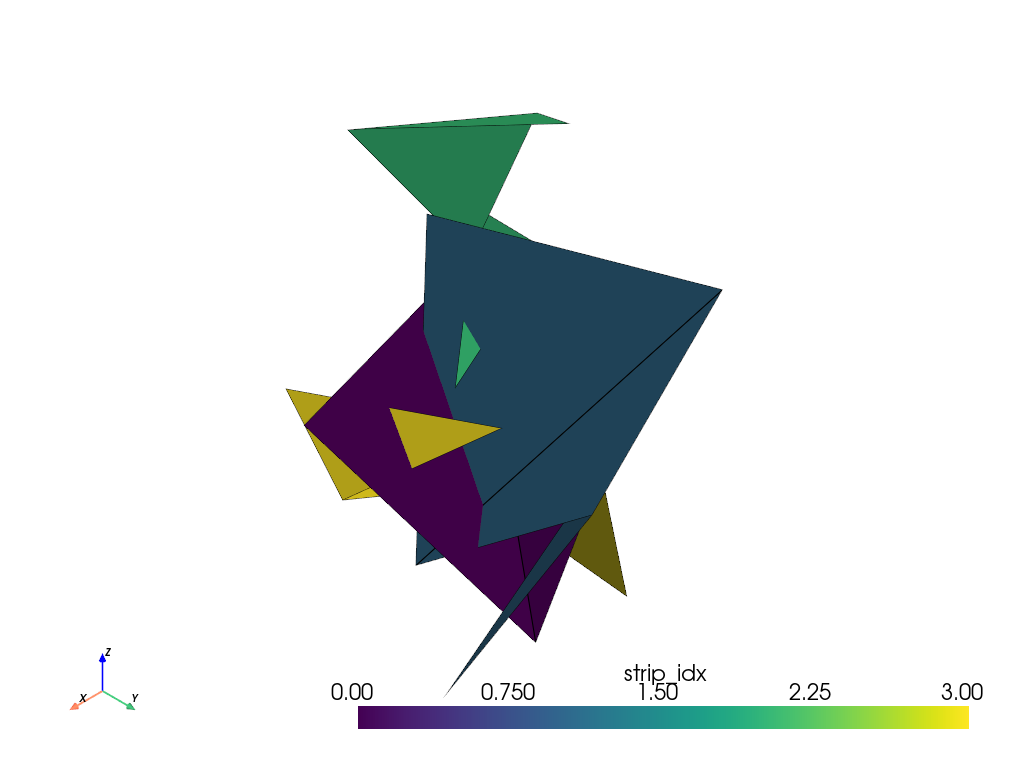
Construct a mesh reusing the
facespv.CellArrayfrom another mesh. The VTK methodsGetPolys,GetLines,GetStrips, andGetVertsreturn the underlyingCellArray``s for the ``faces,lines,strips, andvertsproperties respectively. Reusing cell arrays like this can be a performance optimization for large meshes because it avoids allocating new arrays.>>> small_sphere = pv.Sphere().compute_normals() >>> inflated_points = ( ... small_sphere.points + 0.1 * small_sphere.point_data['Normals'] ... ) >>> larger_sphere = pv.PolyData(inflated_points, faces=small_sphere.GetPolys()) >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(small_sphere, color='red', show_edges=True) >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(larger_sphere, color='blue', opacity=0.3, show_edges=True) >>> pl.show()
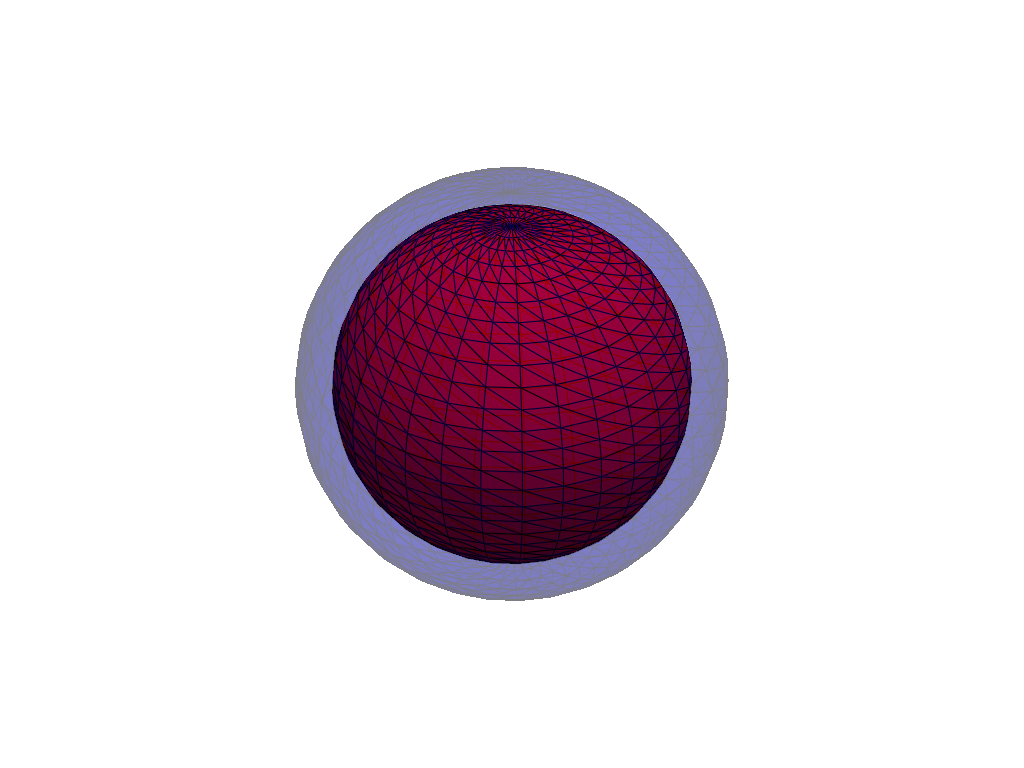
See Create PolyData for more examples.
Methods#
|
Alternate pyvista.PolyData convenience constructor from point and ragged face arrays. |
|
Alternate pyvista.PolyData convenience constructor from point and regular face arrays. |
|
Write a surface mesh to disk. |
Global opt-in to strict n_faces. |
Attributes#
Return the cell normals. |
|
Return the cell normals. |
|
Return the polygonal faces padded connectivity array. |
|
Return a tuple of face arrays. |
|
Return if all the faces of the |
|
Return if the mesh is manifold (no open edges). |
|
Return the lines connectivity array. |
|
Return the number of cells. |
|
Return the number of polygonal faces. |
|
Return the number of line cells. |
|
Return the number of open edges on this mesh. |
|
Return the number of triangle strips. |
|
Return the number of vertex cells. |
|
Return the obbTree of the polydata. |
|
Return the point normals. |
|
Return a face array of point indices when all faces have the same size. |
|
Return or set the strips padded connectivity array. |
|
Return or set the vertex padded connectivity array. |
|
Return the approximate volume of the dataset. |