Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Types of Shading#
Comparison of default, flat shading vs. smooth shading.
from __future__ import annotations
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
PyVista supports two types of shading: flat and smooth shading that uses VTK’s Phong shading algorithm.
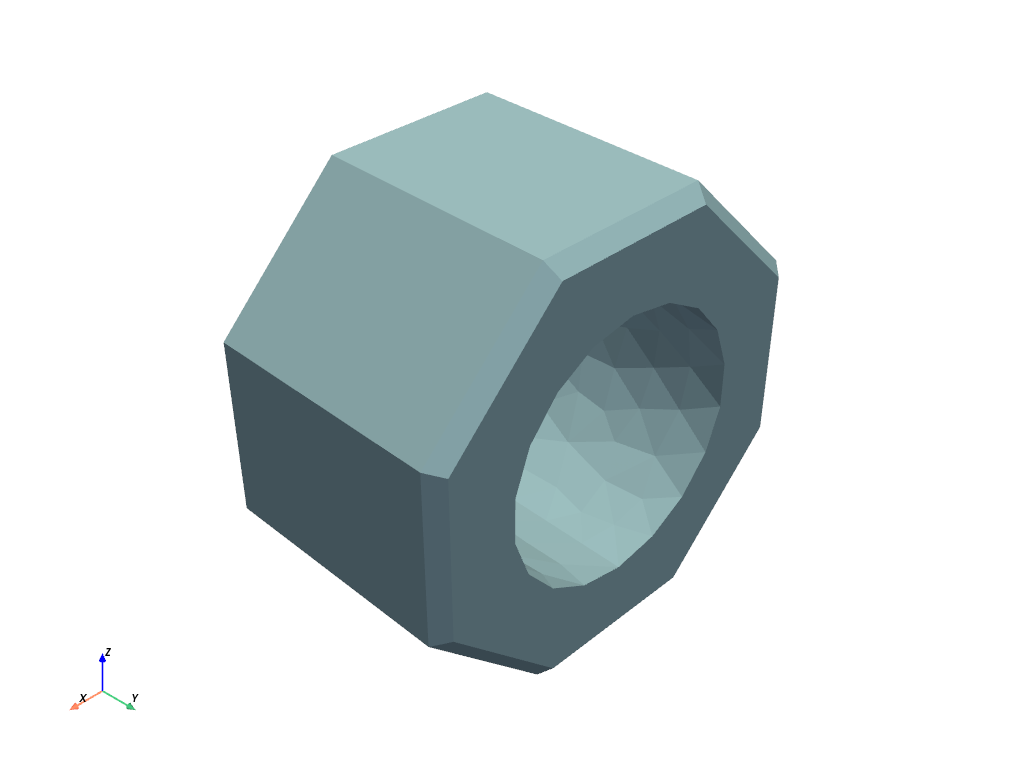
This is a plot with the default flat shading.
Here’s the same sphere with smooth shading.
mesh.plot(smooth_shading=True)
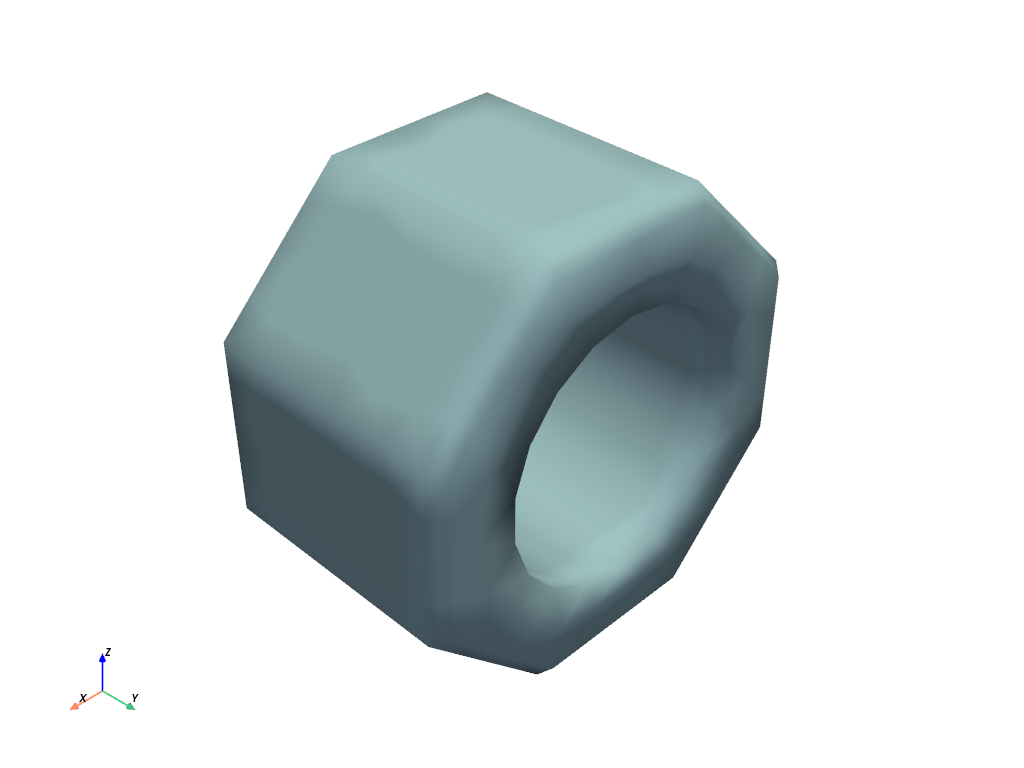
Note how smooth shading makes edges that should be sharp look odd,
it’s because the points of these normals are averaged between two
faces that have a sharp angle between them. You can avoid this by
enabling split_sharp_edges.
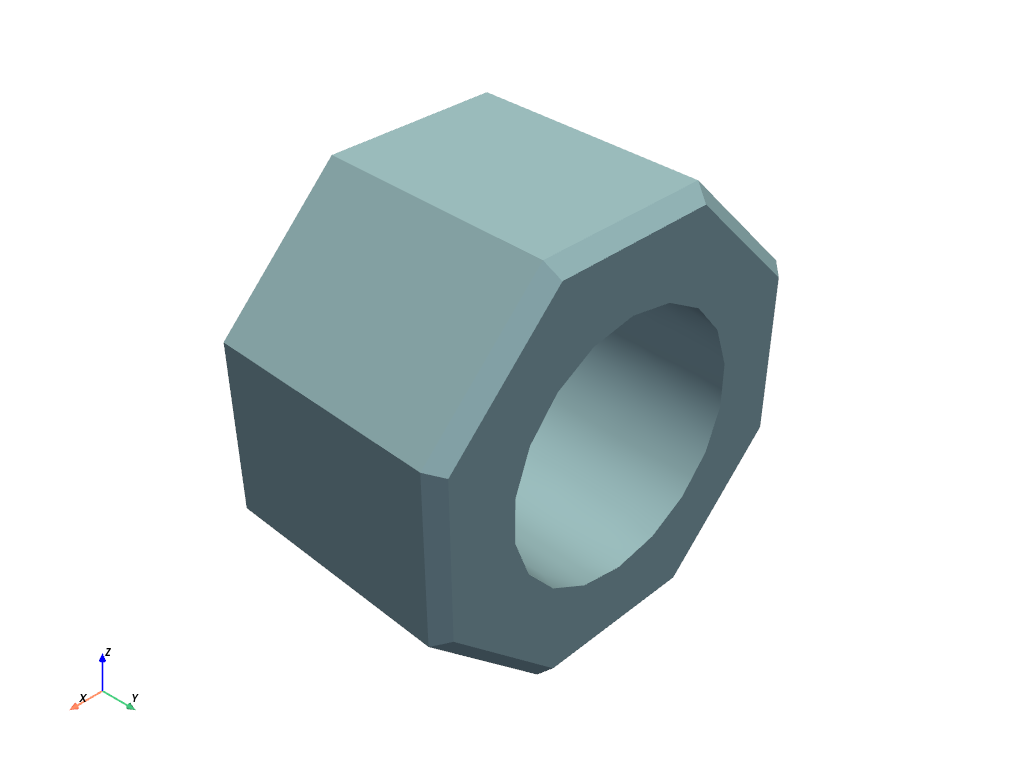
Note
You can configure the splitting angle with the optional
feature_angle keyword argument.
mesh.plot(smooth_shading=True, split_sharp_edges=True)
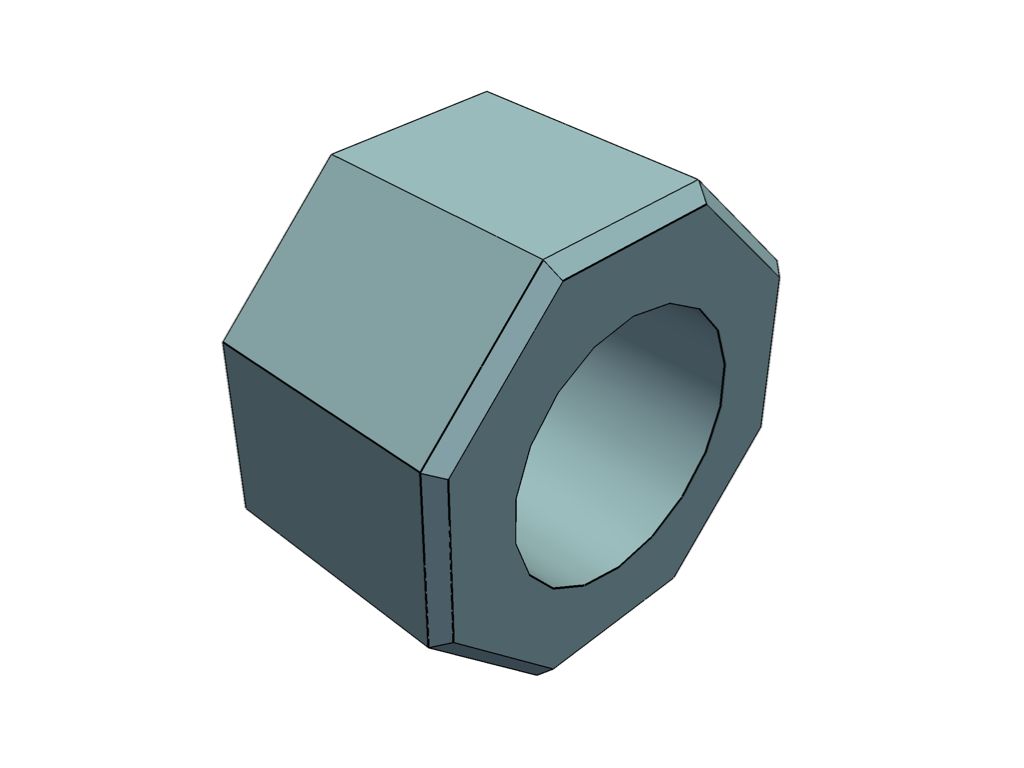
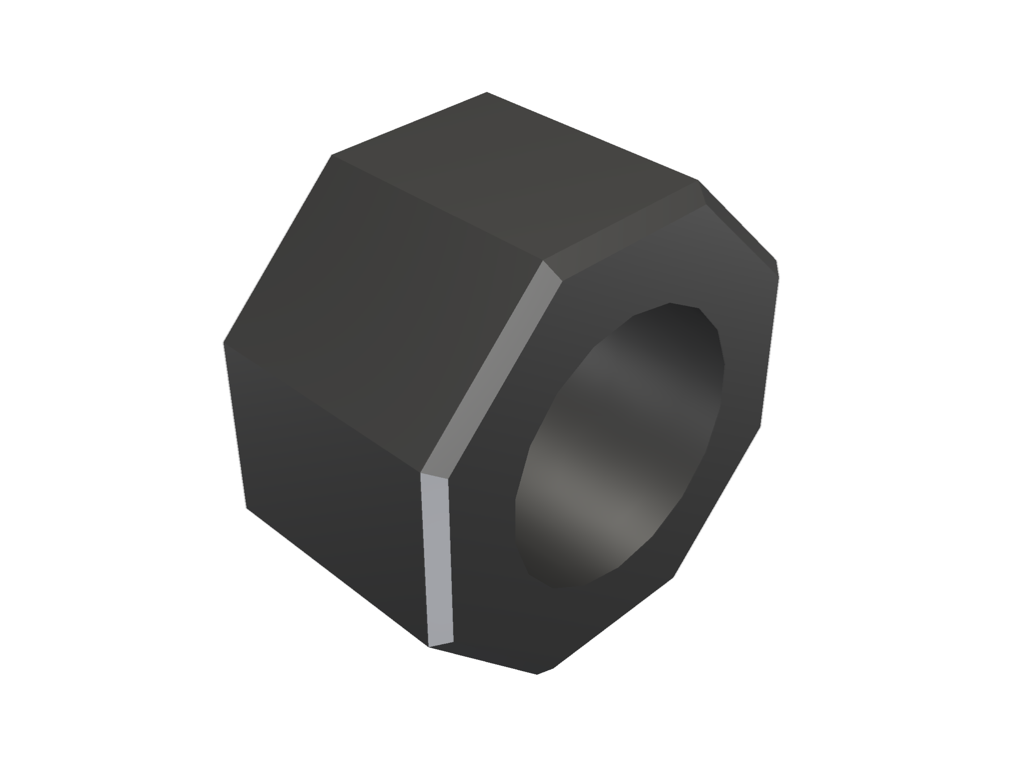
We can even plot the edges that will be split using
extract_feature_edges.
# extract the feature edges exceeding 30 degrees
edges = mesh.extract_feature_edges(
boundary_edges=False,
non_manifold_edges=False,
feature_angle=30,
manifold_edges=False,
)
# plot both the edges and the smoothed mesh
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.enable_anti_aliasing()
pl.add_mesh(mesh, smooth_shading=True, split_sharp_edges=True)
pl.add_mesh(edges, color='k', line_width=5)
pl.show()
The split_sharp_edges keyword argument is compatible with
physically based rendering as well.
# plot both the edges and the smoothed mesh
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.enable_anti_aliasing()
pl.add_mesh(
mesh, color='w', split_sharp_edges=True, pbr=True, metallic=1.0, roughness=0.5
)
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.041 seconds)