pyvista.Label#
- class Label(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
2D label actor with a 3D position coordinate.
Unlike
Text, which uses 2D viewport coordinates to position text in a plot, this class instead uses a 3D position coordinate. This class may be positioned, oriented, and transformed in a manner similar to a 3DActor.In addition, this class supports an additional
relative_positionattribute. In general, it is recommended to simply usepositionwhen positioning aLabelby itself. However, if the position of the label depends on the positioning of another actor, bothpositionandrelative_positionmay be used together. In these cases, thepositionof the label and actor should be kept in-sync. See the examples below.- Parameters:
- text
str,optional Text string to be displayed.
- position
VectorLike[float] Position of the text in XYZ coordinates.
- relative_position
VectorLike[float] Position of the text in XYZ coordinates relative to its
position.- size
int Size of the text label.
- prop
pyvista.TextProperty,optional The property of this actor.
- name
str,optional The name of this actor used when tracking on a plotter.
Added in version 0.45.
- text
See also
Examples
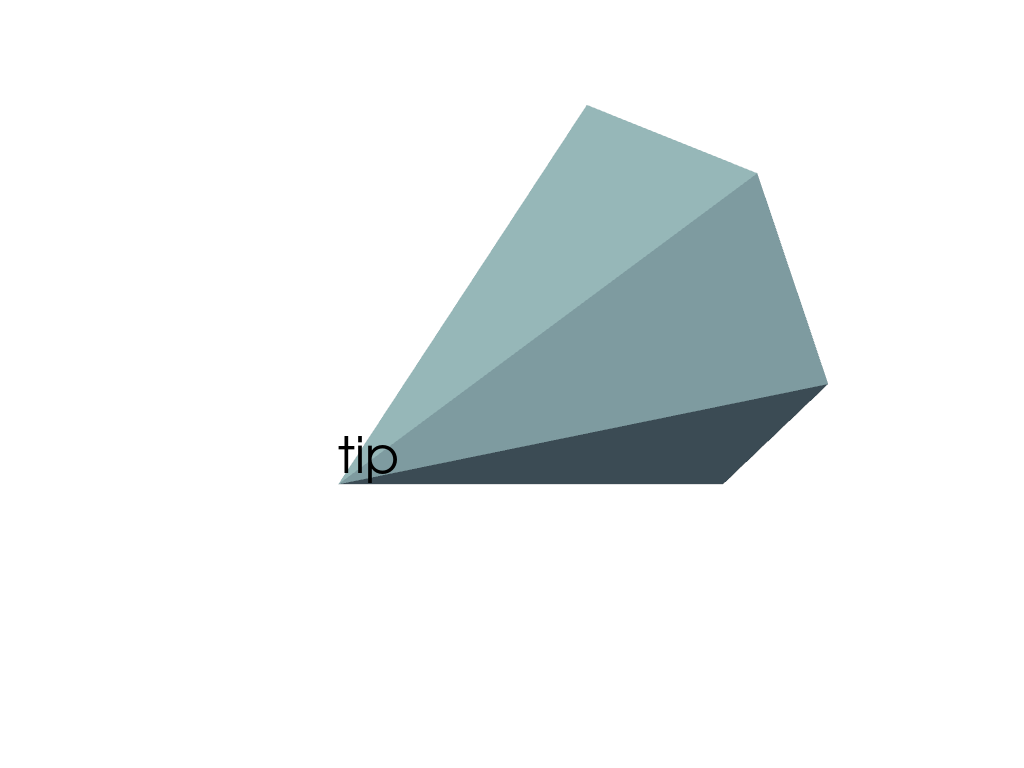
Create a label for a point of interest. Here we add a label to the tip of a cone.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> cone_dataset = pv.Cone() >>> tip = (0.5, 0, 0) >>> label = pv.Label('tip', position=tip)
Plot the mesh and label.
>>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> cone_actor = pl.add_mesh(cone_dataset) >>> _ = pl.add_actor(label) >>> pl.show()
The previous example set the label’s position as the cone’s tip explicitly. However, this means that the two actors now have different positions.
>>> cone_actor.position (0.0, 0.0, 0.0) >>> label.position (0.5, 0.0, 0.0)
And if we change the 3D orientation of the cone and label, the label is no longer positioned at the tip.
>>> cone_actor.orientation = 0, 0, 90 >>> label.orientation = 0, 0, 90 >>> >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_actor(cone_actor) >>> _ = pl.add_actor(label) >>> pl.show()

This is because rotations by
pyvista.Prop3Dare applied before the actor is moved to its final position, and therefore the label’s position is not considered in the rotation. Hence, the final position of the label remains at(0.5, 0.0, 0.0)as it did earlier, despite changing its orientation.If we want the position of the label to have the same positioning relative to the cone, we can instead set its
relative_position.First, reset the label’s position to match the cone’s position.
>>> label.position = cone_actor.position >>> label.position (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
Now set its
relative_positionto the tip of the cone.>>> label.relative_position = tip >>> label.relative_position (0.5, 0.0, 0.0)
Plot the results. The label is now correctly positioned at the tip of the cone. This is because the
relative_positionis considered as part of the rotation.>>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_actor(cone_actor) >>> _ = pl.add_actor(label) >>> pl.show()
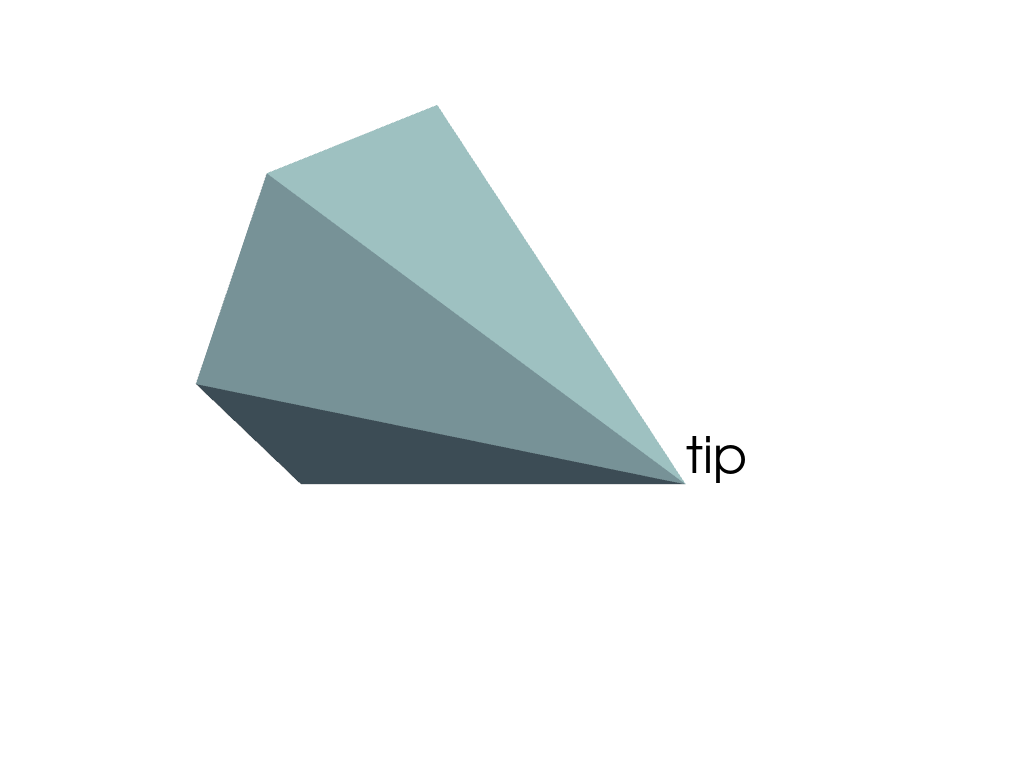

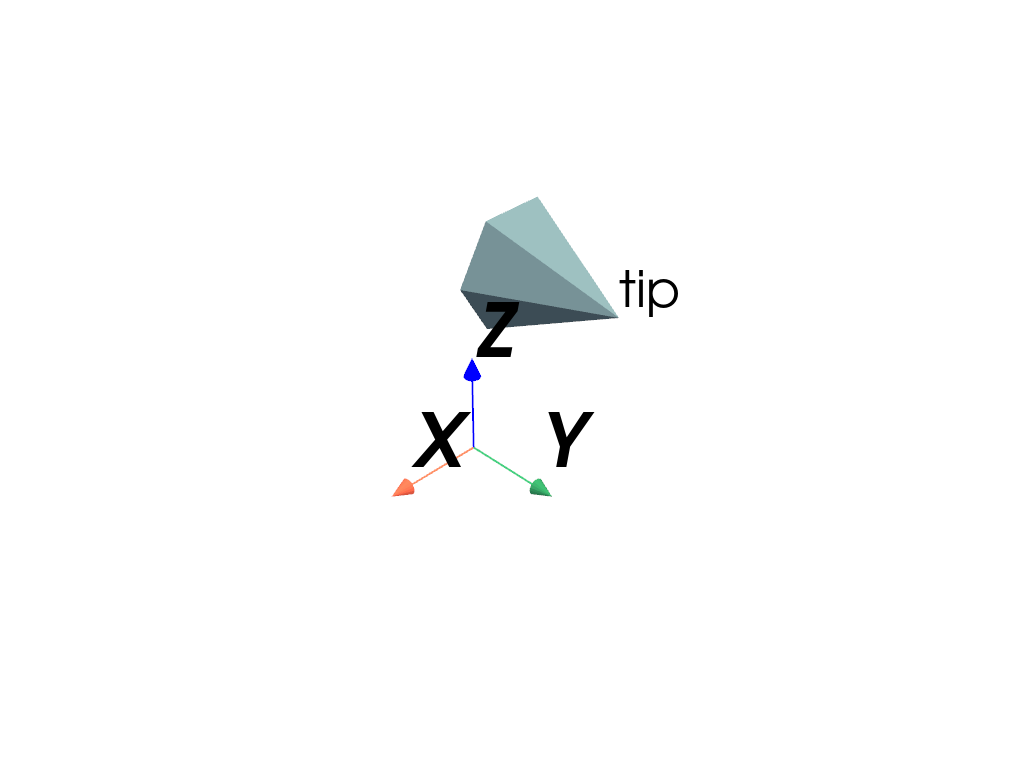
As long as the label and cone’s
pyvista.Prop3Dattributes are modified together and synchronized, the label will remain at the tip of the cone.Modify the position of the label and tip.
>>> cone_actor.position = (1.0, 2.0, 3.0) >>> label.position = (1.0, 2.0, 3.0) >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_actor(cone_actor) >>> _ = pl.add_actor(label) >>> _ = pl.add_axes_at_origin() >>> pl.show()
Methods
Attributes
Position of the label relative to its
position.Size of the text label.