pyvista.PolyDataFilters.ray_trace#
- PolyDataFilters.ray_trace( )[source]#
Perform a single ray trace calculation.
This requires a mesh and a line segment defined by an origin and end_point.
- Parameters:
- originsequence[
float] Start of the line segment.
- end_pointsequence[
float] End of the line segment.
- first_pointbool, default:
False Returns intersection of first point only.
- plotbool, default:
False Whether to plot the ray trace results.
- off_screenbool,
optional Plots off screen when
plot=True. Used for unit testing.
- originsequence[
- Returns:
- intersection_points
numpy.ndarray Location of the intersection points. Empty array if no intersections.
- intersection_cells
numpy.ndarray Indices of the intersection cells. Empty array if no intersections.
- intersection_points
See also
- Visualize the Moeller-Trumbore Algorithm
Example of ray-tracing using the Moeller-Trumbore intersection algorithm.
Examples
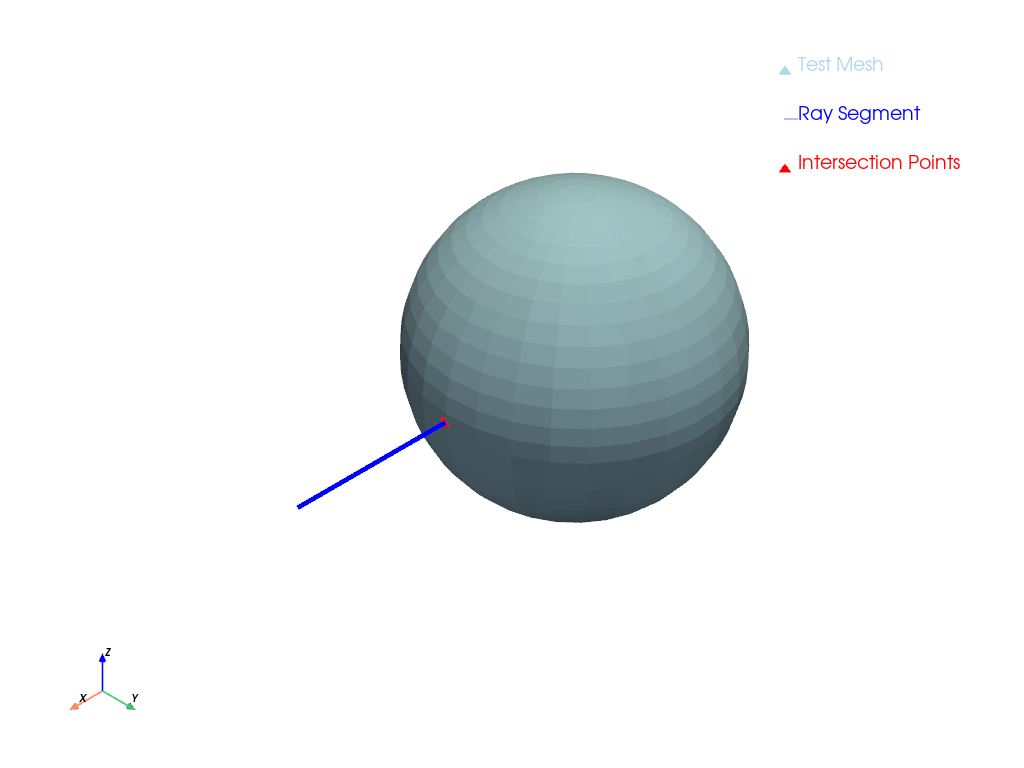
Compute the intersection between a ray from the origin to
[1, 0, 0]and a sphere with radius 0.5 centered at the origin.>>> import pyvista as pv >>> sphere = pv.Sphere() >>> point, cell = sphere.ray_trace([0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], first_point=True) >>> f'Intersected at {point[0]:.3f} {point[1]:.3f} {point[2]:.3f}' 'Intersected at 0.499 0.000 0.000'
Show a plot of the ray trace.
>>> point, cell = sphere.ray_trace([0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], plot=True)
See Ray Tracing for more examples using this filter.