pyvista.Plotter.add_plane_widget#
- Plotter.add_plane_widget(
- callback,
- normal='x',
- origin=None,
- bounds=None,
- factor=1.25,
- color=None,
- assign_to_axis=None,
- tubing: bool = False,
- outline_translation: bool = False,
- origin_translation: bool = True,
- implicit: bool = True,
- pass_widget: bool = False,
- test_callback: bool = True,
- normal_rotation: bool = True,
- interaction_event: pyvista.InteractionEventType = 'end',
- outline_opacity=None,
Add a plane widget to the scene.
This is useless without a callback function. You can pass a callable function that takes two arguments, the normal and origin of the plane in that order output from this widget, and performs a task with that plane.
- Parameters:
- callback
callable() The method called every time the plane is updated. Takes two arguments, the normal and origin of the plane in that order.
- normal
strortuple(float) The starting normal vector of the plane.
- origin
tuple(float) The starting coordinate of the center of the plane.
- bounds
tuple(float) Length 6 tuple of the bounding box where the widget is placed.
- factor
float,optional An inflation factor to expand on the bounds when placing.
- color
ColorLike,optional Either a string, rgb list, or hex color string.
- assign_to_axis
strorint,optional Assign the normal of the plane to be parallel with a given axis: options are
(0, 'x'),(1, 'y'), or(2, 'z').- tubingbool,
optional When using an implicit plane widget, this controls whether or not tubing is shown around the plane’s boundaries.
- outline_translationbool,
optional If
False, the plane widget cannot be translated and is strictly placed at the given bounds. Only valid when using an implicit plane.- origin_translationbool,
optional If
False, the plane widget cannot be translated by its origin and is strictly placed at the given origin. Only valid when using an implicit plane.- implicitbool,
optional When
True, a vtkImplicitPlaneWidget is used and whenFalse, a vtkPlaneWidget is used.- pass_widgetbool,
optional If
True, the widget will be passed as the last argument of the callback.- test_callbackbool,
optional If
True, run the callback function after the widget is created.- normal_rotationbool,
optional Set the opacity of the normal vector arrow to 0 such that it is effectively disabled. This prevents the user from rotating the normal. This is forced to
Falsewhenassign_to_axisis set.- interaction_event
InteractionEventType,optional The VTK interaction event to use for triggering the callback. Accepts either the strings
'start','end','always'or a vtkCommand.EventIds.Changed in version 0.38.0: Now accepts either strings and vtkCommand.EventIds.
- outline_opacitybool or
float,optional Set the visible of outline. Only valid when using an implicit plane. Either a bool or float.
Added in version 0.44.0.
- callback
- Returns:
- outputvtkImplicitPlaneWidget | vtkPlaneWidget
Plane widget.
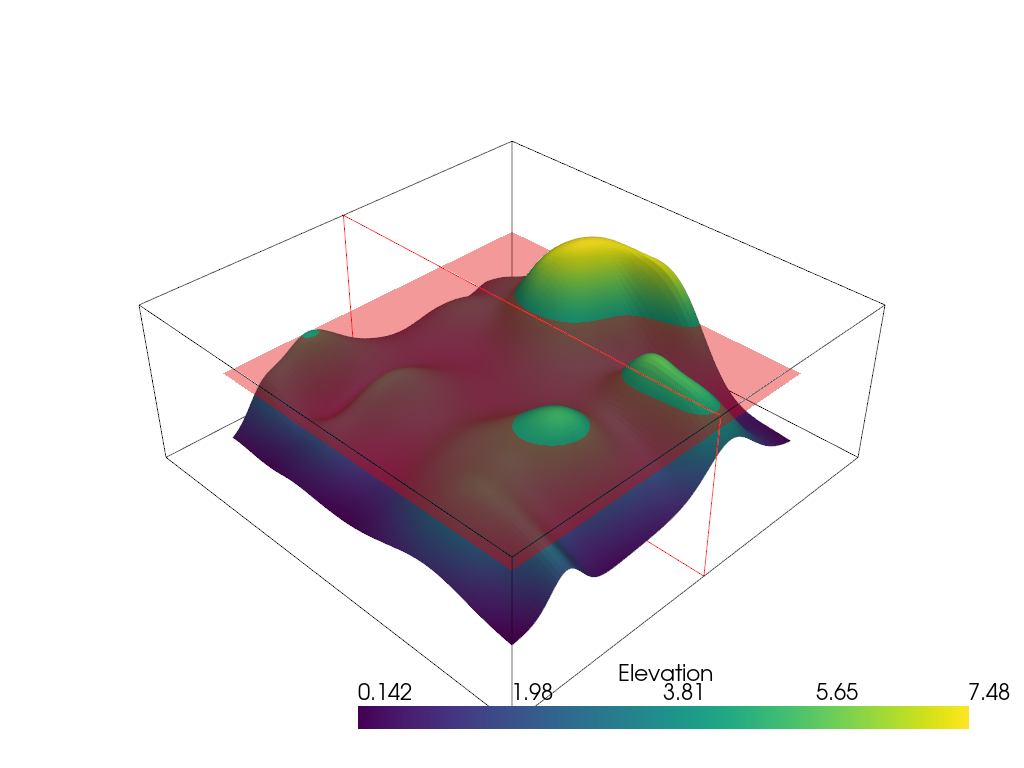
Examples
Shows an interactive plane moving along the x-axis in the random-hill example, which is used to mark the max altitude at a particular distance x.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> from pyvista import examples >>> mesh = examples.load_random_hills() >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(mesh) >>> def callback(normal, origin): ... slc = mesh.slice(normal=normal, origin=origin) ... origin = list(origin) ... origin[2] = slc.bounds.z_max ... peak_plane = pv.Plane( ... center=origin, ... direction=[0, 0, 1], ... i_size=20, ... j_size=20, ... ) ... _ = pl.add_mesh(peak_plane, name='Peak', color='red', opacity=0.4) >>> _ = pl.add_plane_widget(callback, normal_rotation=False) >>> pl.show()