pyvista.PolyDataFilters.smooth#
- PolyDataFilters.smooth(
- n_iter=20,
- relaxation_factor=0.01,
- convergence=0.0,
- edge_angle=15,
- feature_angle=45,
- boundary_smoothing: bool = True,
- feature_smoothing: bool = False,
- inplace: bool = False,
- progress_bar: bool = False,
Adjust point coordinates using Laplacian smoothing.
The effect is to “relax” the mesh, making the cells better shaped and the vertices more evenly distributed.
- Parameters:
- n_iter
int, default: 20 Number of iterations for Laplacian smoothing.
- relaxation_factor
float, default: 0.01 Relaxation factor controls the amount of displacement in a single iteration. Generally a lower relaxation factor and higher number of iterations is numerically more stable.
- convergence
float, default: 0.0 Convergence criterion for the iteration process. Smaller numbers result in more smoothing iterations. Range from (0 to 1).
- edge_angle
float, default: 15 Edge angle to control smoothing along edges (either interior or boundary).
- feature_angle
float, default: 45 Feature angle for sharp edge identification.
- boundary_smoothingbool, default:
True Flag to control smoothing of boundary edges. When
True, boundary edges remain fixed.- feature_smoothingbool, default:
False Flag to control smoothing of feature edges. When
True, boundary edges remain fixed as defined byfeature_angleandedge_angle.- inplacebool, default:
False Updates mesh in-place.
- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- n_iter
- Returns:
pyvista.PolyDataSmoothed mesh.
Examples
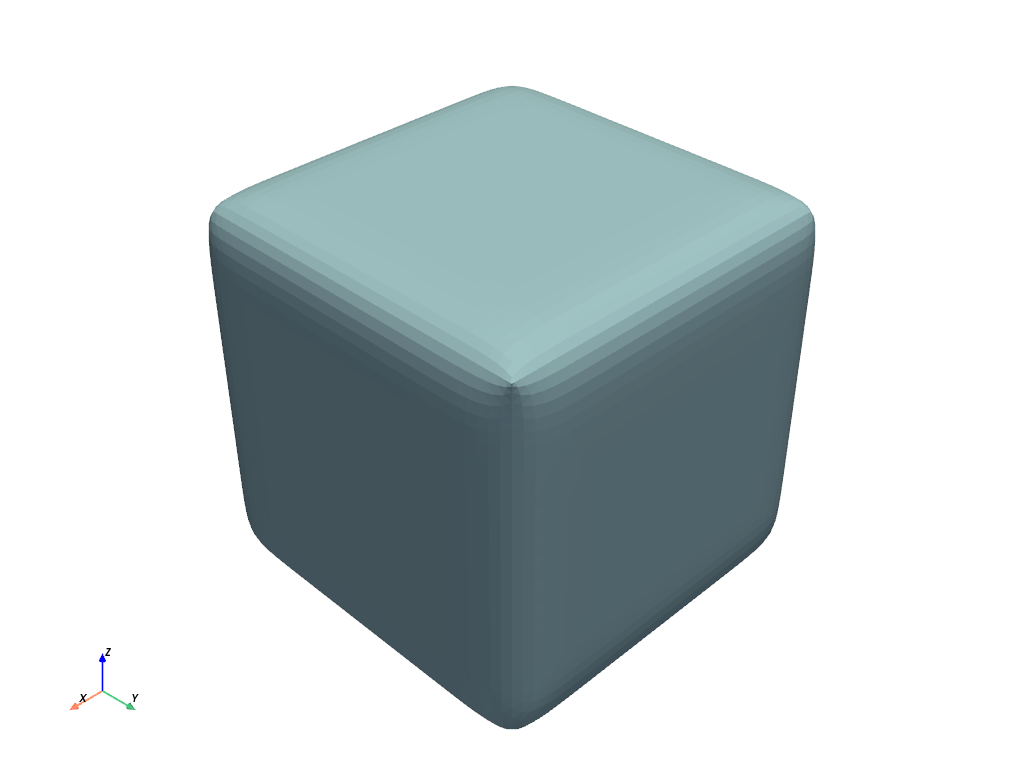
Smooth the edges of an all triangular cube
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> cube = pv.Cube().triangulate().subdivide(5) >>> smooth_cube = cube.smooth(n_iter=1000, feature_smoothing=False) >>> n_edge_cells = cube.extract_feature_edges().n_cells >>> n_smooth_cells = smooth_cube.extract_feature_edges().n_cells >>> f'Sharp Edges on Cube: {n_edge_cells}' 'Sharp Edges on Cube: 384' >>> f'Sharp Edges on Smooth Cube: {n_smooth_cells}' 'Sharp Edges on Smooth Cube: 12' >>> smooth_cube.plot()
See Surface Smoothing for more examples using this filter.