pyvista.DataSetFilters.select_enclosed_points#
- DataSetFilters.select_enclosed_points(
- surface: PolyData,
- tolerance: float = 0.001,
- inside_out: bool = False,
- check_surface: bool = True,
- progress_bar: bool = False,
Mark points as to whether they are inside a closed surface.
This evaluates all the input points to determine whether they are in an enclosed surface. The filter produces a (0,1) mask (in the form of a vtkDataArray) that indicates whether points are outside (mask value=0) or inside (mask value=1) a provided surface. (The name of the output vtkDataArray is
"SelectedPoints".)This filter produces and output data array, but does not modify the input dataset. If you wish to extract cells or poinrs, various threshold filters are available (i.e., threshold the output array).
Warning
The filter assumes that the surface is closed and manifold. A boolean flag can be set to force the filter to first check whether this is true. If
Falseand not manifold, an error will be raised.- Parameters:
- surface
pyvista.PolyData Set the surface to be used to test for containment. This must be a
pyvista.PolyDataobject.- tolerance
float, default: 0.001 The tolerance on the intersection. The tolerance is expressed as a fraction of the bounding box of the enclosing surface.
- inside_outbool, default:
False By default, points inside the surface are marked inside or sent to the output. If
inside_outisTrue, then the points outside the surface are marked inside.- check_surfacebool, default:
True Specify whether to check the surface for closure. When
True, the algorithm first checks to see if the surface is closed and manifold. If the surface is not closed and manifold, a runtime error is raised.- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- surface
- Returns:
pyvista.PolyDataMesh containing the
point_data['SelectedPoints']array.
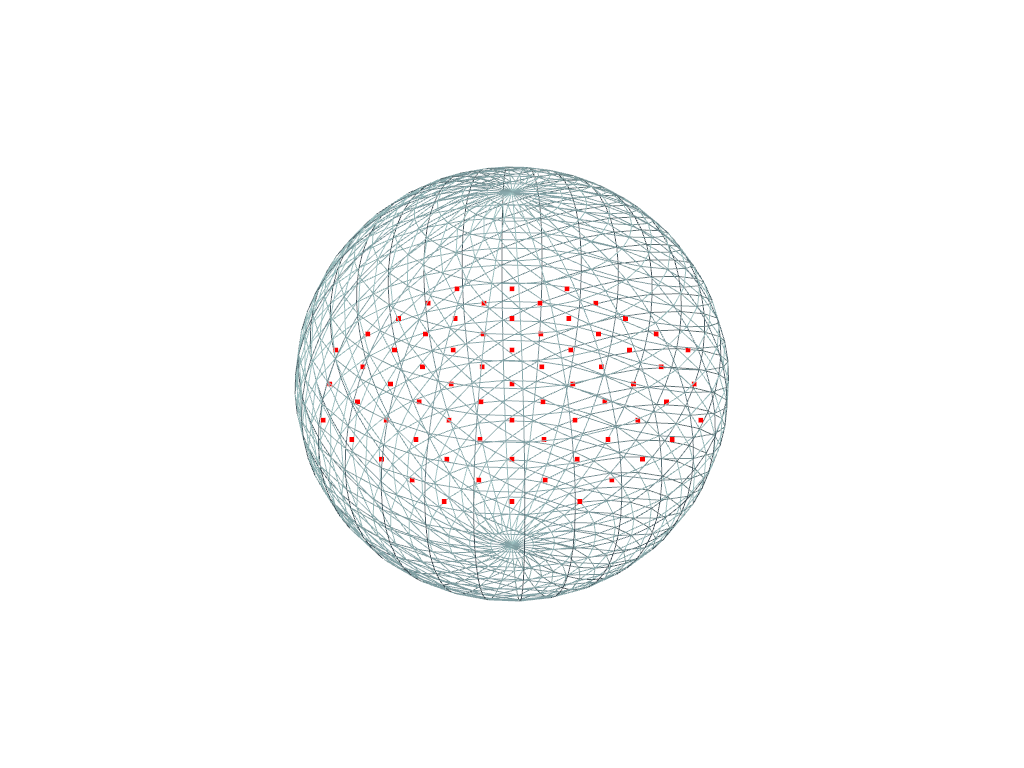
Examples
Determine which points on a plane are inside a manifold sphere surface mesh. Extract these points using the
DataSetFilters.extract_points()filter and then plot them.>>> import pyvista as pv >>> sphere = pv.Sphere() >>> plane = pv.Plane() >>> selected = plane.select_enclosed_points(sphere) >>> pts = plane.extract_points( ... selected['SelectedPoints'].view(bool), ... adjacent_cells=False, ... ) >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(sphere, style='wireframe') >>> _ = pl.add_points(pts, color='r') >>> pl.show()