pyvista.ImageDataFilters.median_smooth#
- ImageDataFilters.median_smooth(
- kernel_size=(3, 3, 3),
- scalars=None,
- preference='point',
- progress_bar: bool = False,
Smooth data using a median filter.
The Median filter that replaces each pixel with the median value from a rectangular neighborhood around that pixel. Neighborhoods can be no more than 3 dimensional. Setting one axis of the neighborhood kernelSize to 1 changes the filter into a 2D median.
See vtkImageMedian3D for more details.
- Parameters:
- kernel_sizesequence[
int], default: (3, 3, 3) Size of the kernel in each dimension (units of voxels), for example
(x_size, y_size, z_size). Default is a 3D median filter. If you want to do a 2D median filter, set the size to 1 in the dimension you don’t want to filter over.- scalars
str,optional Name of scalars to process. Defaults to currently active scalars.
- preference
str, default: “point” When scalars is specified, this is the preferred array type to search for in the dataset. Must be either
'point'or'cell'.- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- kernel_sizesequence[
- Returns:
pyvista.ImageDataUniform grid with smoothed scalars.
Warning
Applying this filter to cell data will send the output to a new point array with the same name, overwriting any existing point data array with the same name.
Examples
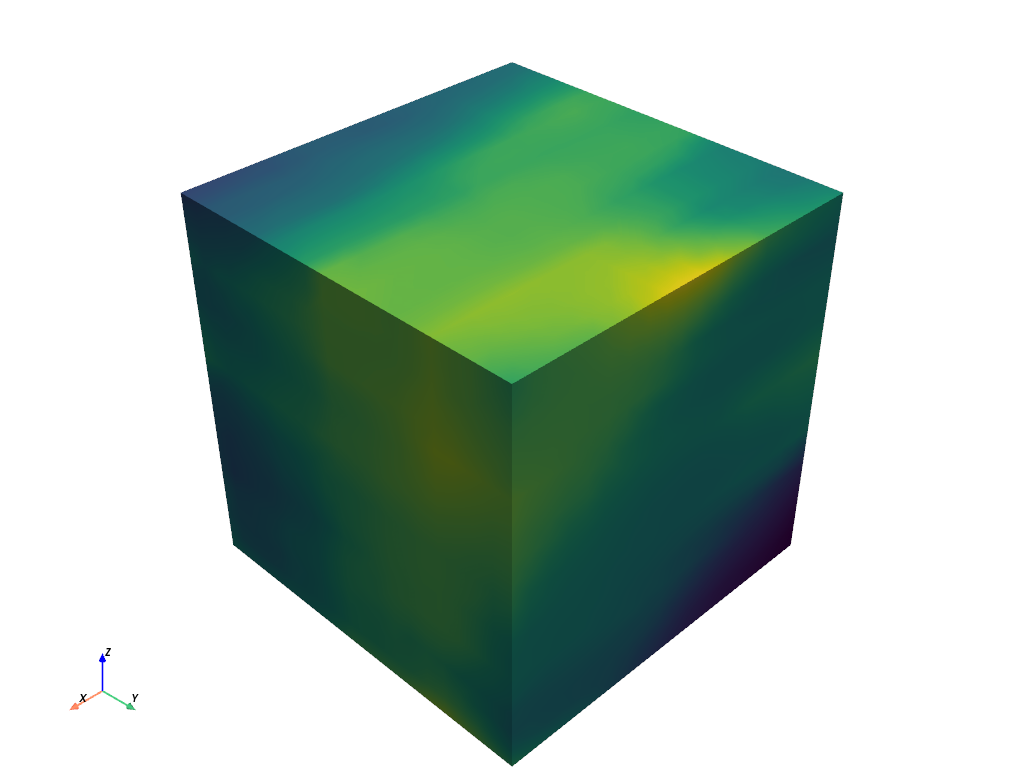
First, create sample data to smooth. Here, we use
pyvista.perlin_noise()to create meaningful data.>>> import numpy as np >>> import pyvista as pv >>> noise = pv.perlin_noise(0.1, (2, 5, 8), (0, 0, 0)) >>> grid = pv.sample_function(noise, [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1], dim=(20, 20, 20)) >>> grid.plot(show_scalar_bar=False)
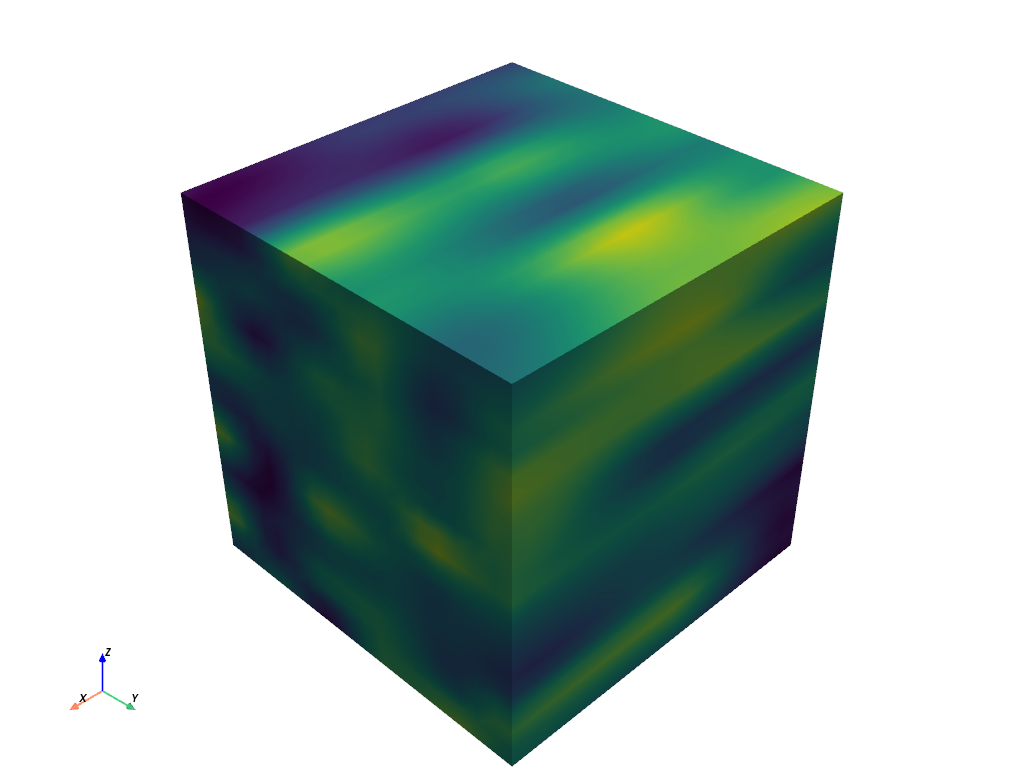
Next, smooth the sample data.
>>> smoothed = grid.median_smooth(kernel_size=(10, 10, 10)) >>> smoothed.plot(show_scalar_bar=False)