pyvista.UnstructuredGrid#
- class UnstructuredGrid(*args, **kwargs)[source]#
Dataset used for arbitrary combinations of all possible cell types.
Can be initialized by the following:
Creating an empty grid
From a vtkPolyData or vtkStructuredGrid object
From cell, cell types, and point arrays
From a file
- Parameters:
- args
str, vtkUnstructuredGrid, iterable See examples below.
- deepbool, default:
False Whether to deep copy a vtkUnstructuredGrid object. Default is
False. Keyword only.- validatebool |
str| sequence[str], default:False Validate the mesh using
validate_mesh()after initialization. Set this toTrueto validate all fields, or specify any combination of fields allowed byvalidate_mesh.Added in version 0.47.
- args
Examples
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> from pyvista import examples >>> import vtk
Create an empty grid
>>> grid = pv.UnstructuredGrid()
Copy a vtkUnstructuredGrid
>>> vtkgrid = vtk.vtkUnstructuredGrid() >>> grid = pv.UnstructuredGrid(vtkgrid)
From a filename.
>>> grid = pv.UnstructuredGrid(examples.hexbeamfile) >>> grid.plot(show_edges=True)
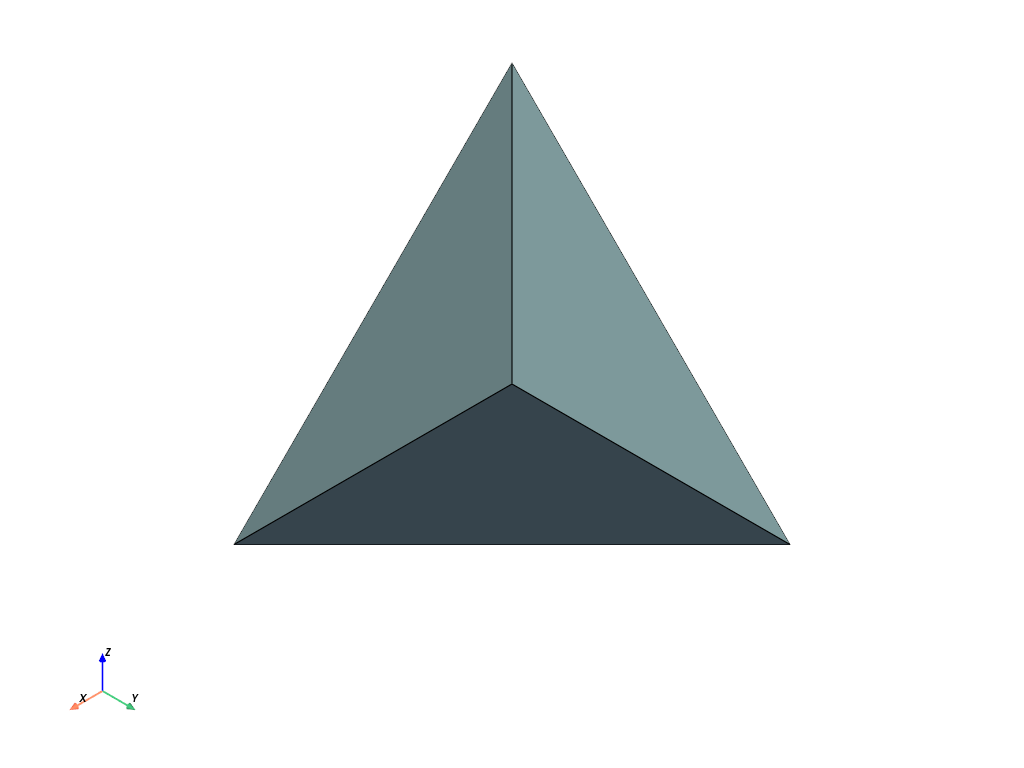
From arrays. Here we create a single tetrahedron.
>>> cells = [4, 0, 1, 2, 3] >>> celltypes = [pv.CellType.TETRA] >>> points = [ ... [1.0, 1.0, 1.0], ... [1.0, -1.0, -1.0], ... [-1.0, 1.0, -1.0], ... [-1.0, -1.0, 1.0], ... ] >>> grid = pv.UnstructuredGrid(cells, celltypes, points) >>> grid.plot(show_edges=True)

See the Creating an Unstructured Grid example for more details on creating unstructured grids within PyVista.
Methods#
Cast to an explicit structured grid. |
|
|
Return a copy of the unstructured grid containing only linear cells. |
Attributes#
Return the cell connectivity as a numpy array. |
|
Return the cell data as a numpy object. |
|
Return a dictionary that contains all cells mapped from cell types. |
|
Return the cell types array. |
|
Return polyhedron face locations. |
|
Return the polyhedron faces. |
|
Return the cell locations array. |
|
Return the polyhedron face locations. |
|
Return the polyhedron faces. |