pyvista.AxesGeometrySource.symmetric_bounds#
- property AxesGeometrySource.symmetric_bounds: bool[source]#
Enable or disable symmetry in the axes bounds.
This option is similar to
symmetric, except instead of making the axes parts symmetric, only the bounds of the axes are made to be symmetric. This is achieved by adding a single invisible cell to each tip dataset along each axis to simulate the symmetry. Setting this parameter primarily affects camera positioning and is useful if the axes are used as a widget, as it allows for the axes to rotate about its origin.Examples
Get the symmetric bounds of the axes.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> axes_geometry_source = pv.AxesGeometrySource(symmetric_bounds=True) >>> axes_geometry_source.output.bounds BoundsTuple(x_min = -1.0, x_max = 1.0, y_min = -1.0, y_max = 1.0, z_min = -1.0, z_max = 1.0)
>>> axes_geometry_source.output.center (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
Get the asymmetric bounds.
>>> axes_geometry_source.symmetric_bounds = False >>> axes_geometry_source.output.bounds BoundsTuple(x_min = -0.1, x_max = 1.0, y_min = -0.1, y_max = 1.0, z_min = -0.1, z_max = 1.0)
>>> axes_geometry_source.output.center (0.45, 0.45, 0.45)
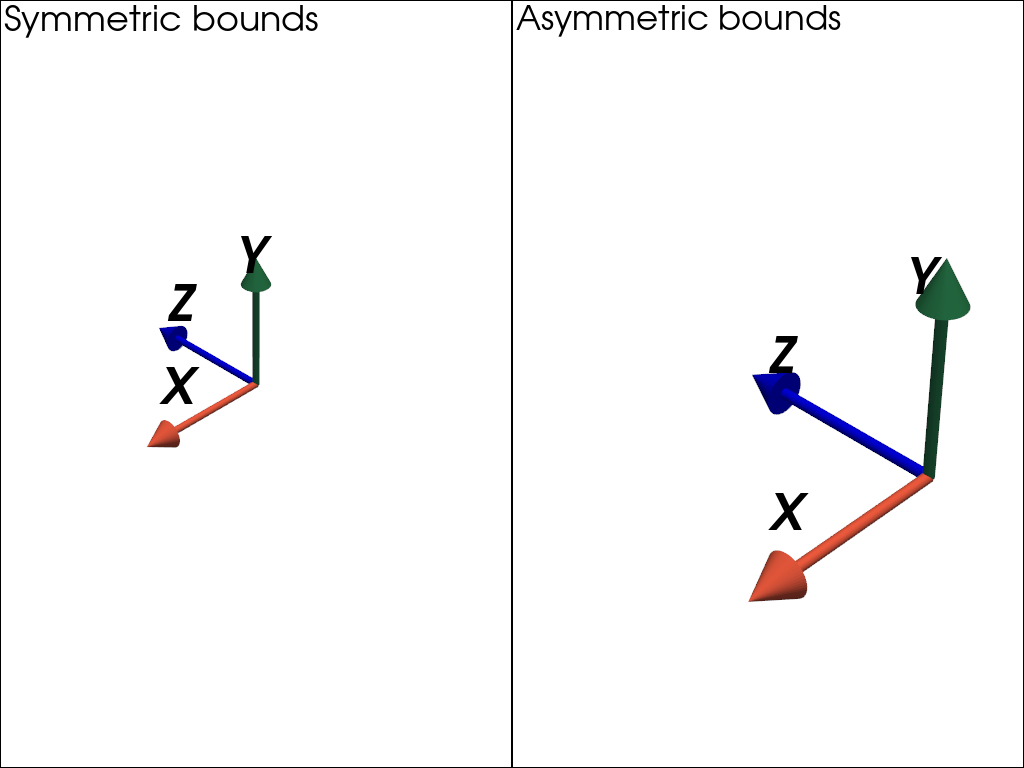
Show the difference in camera positioning with and without symmetric bounds. Orientation is added for visualization.
Create actors.
>>> axes_sym = pv.AxesAssembly(orientation=(90, 0, 0), symmetric_bounds=True) >>> axes_asym = pv.AxesAssembly(orientation=(90, 0, 0), symmetric_bounds=False)
Show multi-window plot.
>>> pl = pv.Plotter(shape=(1, 2)) >>> pl.subplot(0, 0) >>> _ = pl.add_text('Symmetric bounds') >>> _ = pl.add_actor(axes_sym) >>> pl.subplot(0, 1) >>> _ = pl.add_text('Asymmetric bounds') >>> _ = pl.add_actor(axes_asym) >>> pl.show()