Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Volume Rendering#
Volume render uniform mesh types like pyvista.ImageData or 3D
NumPy arrays.
This also explores how to extract a volume of interest (VOI) from a
pyvista.ImageData using the
pyvista.ImageDataFilters.extract_subset() filter.
Simple Volume Render#
Opacity Mappings#
Or use the pyvista.Plotter.add_volume() method like below.
Note that here we use a non-default opacity mapping to a sigmoid:
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_volume(vol, cmap='bone', opacity='sigmoid')
pl.camera_position = cpos
pl.show()
You can also use a custom opacity mapping
opacity = [0, 0, 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1]
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_volume(vol, cmap='viridis', opacity=opacity)
pl.camera_position = cpos
pl.show()

We can also use a shading technique when volume rendering with the shade
option
pl = pv.Plotter(shape=(1, 2))
pl.add_volume(vol, cmap='viridis', opacity=opacity, shade=False)
pl.add_text('No shading')
pl.camera_position = cpos
pl.subplot(0, 1)
pl.add_volume(vol, cmap='viridis', opacity=opacity, shade=True)
pl.add_text('Shading')
pl.link_views()
pl.show()

Cool Volume Examples#
Here are a few more cool volume rendering examples.
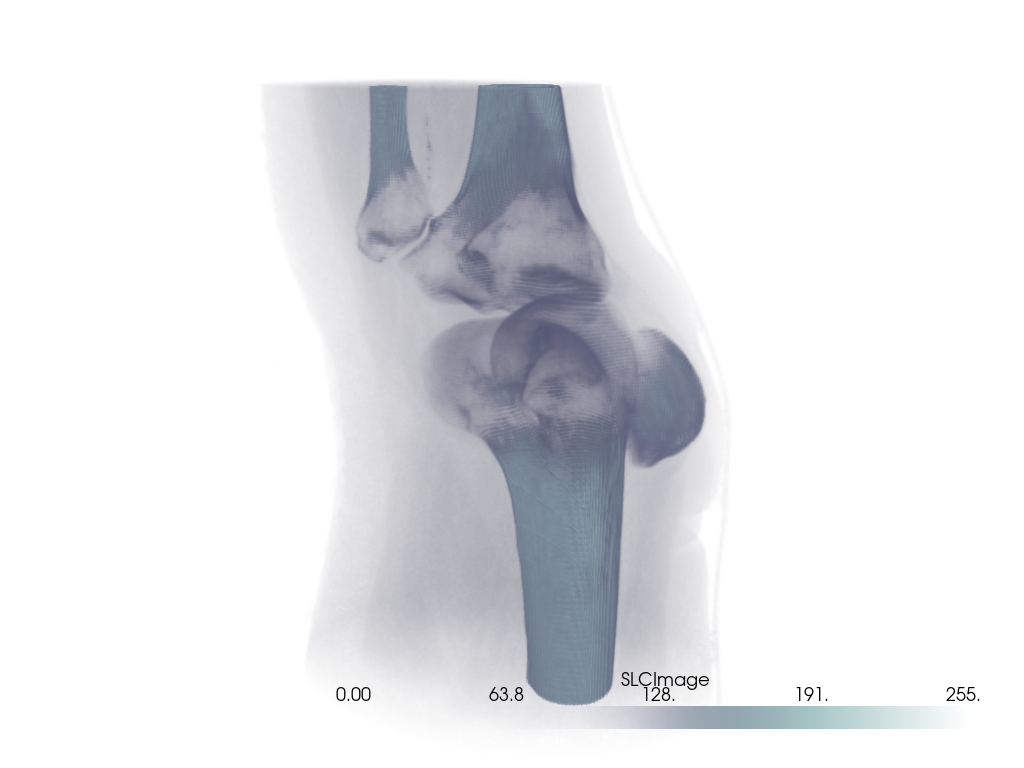
Head Dataset#
head = examples.download_head()
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_volume(head, cmap='cool', opacity='sigmoid_6', show_scalar_bar=False)
pl.camera_position = [(-228.0, -418.0, -158.0), (94.0, 122.0, 82.0), (-0.2, -0.3, 0.9)]
pl.camera.zoom(1.5)
pl.show()

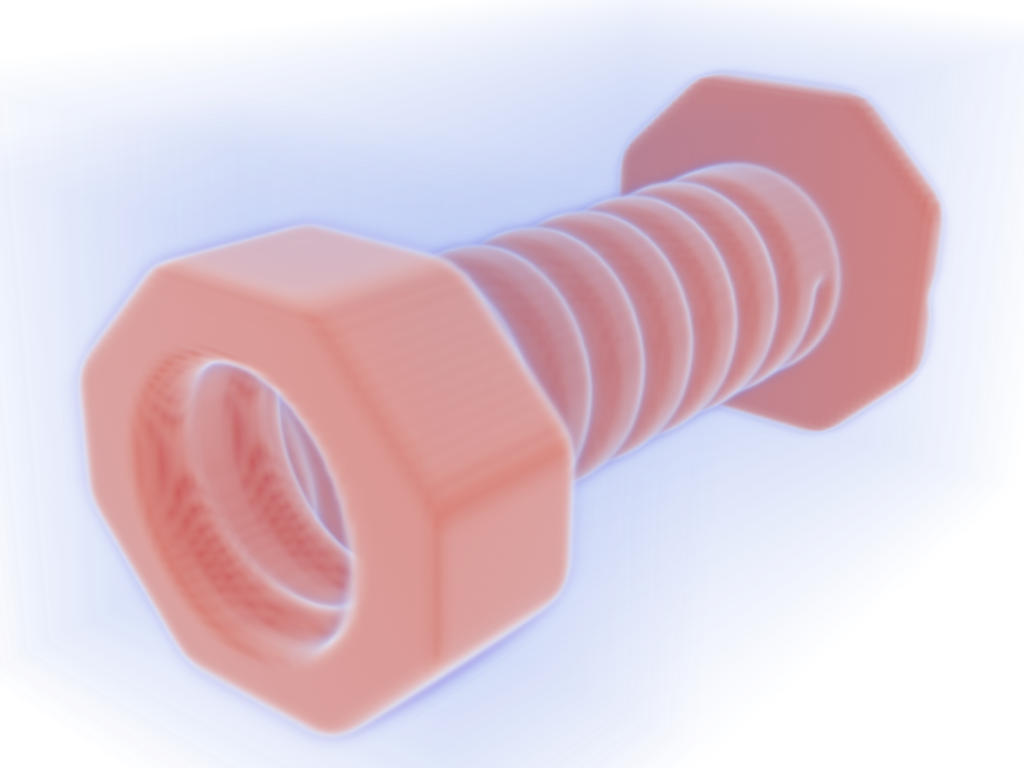
Bolt-Nut MultiBlock Dataset#
Note
See how we set interpolation to 'linear' here to smooth out scalars of
each individual cell to make a more appealing plot. Two actor are returned
by add_volume because bolt_nut is a pyvista.MultiBlock
dataset.
bolt_nut = examples.download_bolt_nut()
pl = pv.Plotter()
actors = pl.add_volume(bolt_nut, cmap='coolwarm', opacity='sigmoid_5', show_scalar_bar=False)
actors[0].prop.interpolation_type = 'linear'
actors[1].prop.interpolation_type = 'linear'
pl.camera_position = [(127.4, -68.3, 88.2), (30.3, 54.3, 26.0), (-0.25, 0.28, 0.93)]
cpos = pl.show(return_cpos=True)
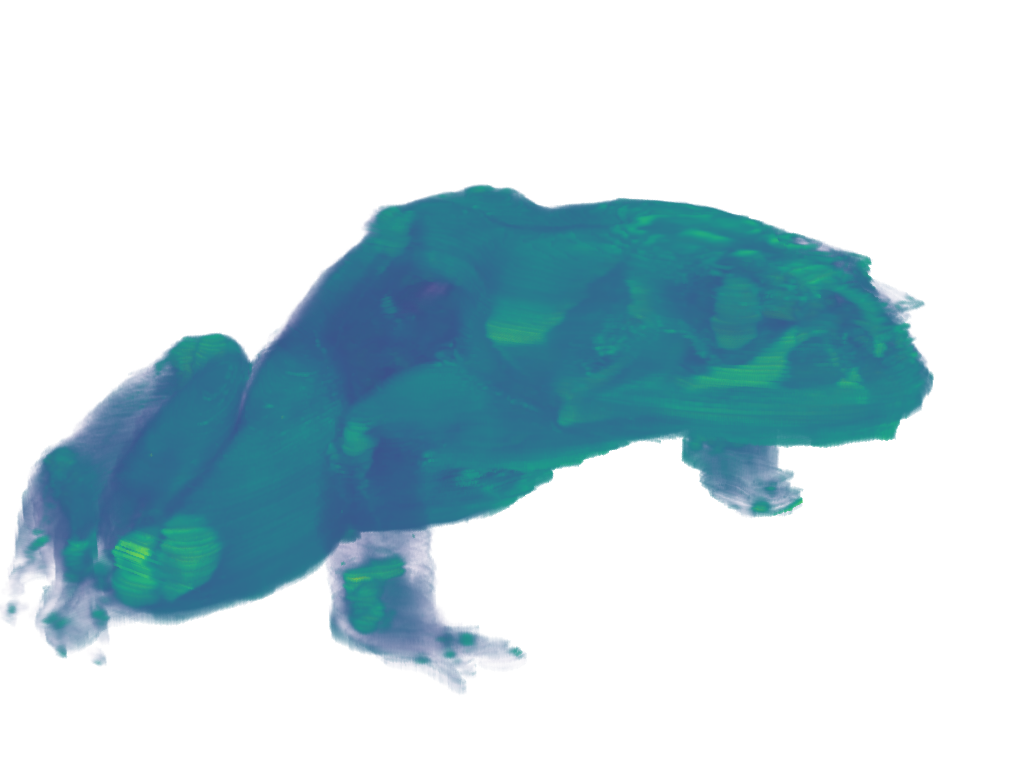
Frog Dataset#
frog = examples.download_frog()
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_volume(frog, cmap='viridis', opacity='sigmoid_6', show_scalar_bar=False)
pl.camera_position = [(929.0, 1067.0, -278.9), (249.5, 234.5, 101.25), (-0.2048, -0.2632, -0.9427)]
pl.camera.zoom(1.5)
pl.show()

Extracting a VOI#
Use the pyvista.ImageDataFilters.extract_subset() filter to extract
a volume of interest/subset volume to volume render. This is ideal when
dealing with particularly large volumes and you want to volume render only
a specific region.
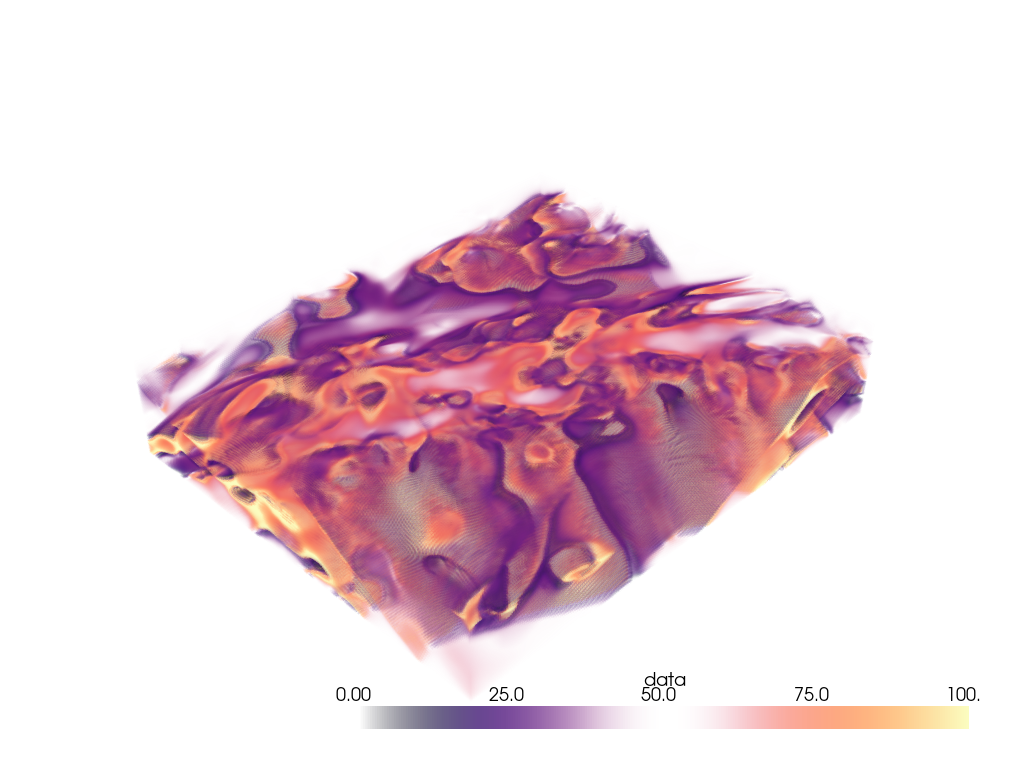
Woah, that’s a big volume. We probably don’t want to volume render the whole thing. So let’s extract a region of interest under the volcano.
The region we will extract will be between nodes 175 and 200 on the x-axis, between nodes 105 and 132 on the y-axis, and between nodes 98 and 170 on the z-axis.
voi = large_vol.extract_subset([175, 200, 105, 132, 98, 170])
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(large_vol.outline(), color='k')
pl.add_mesh(voi, cmap='magma')
pl.show()
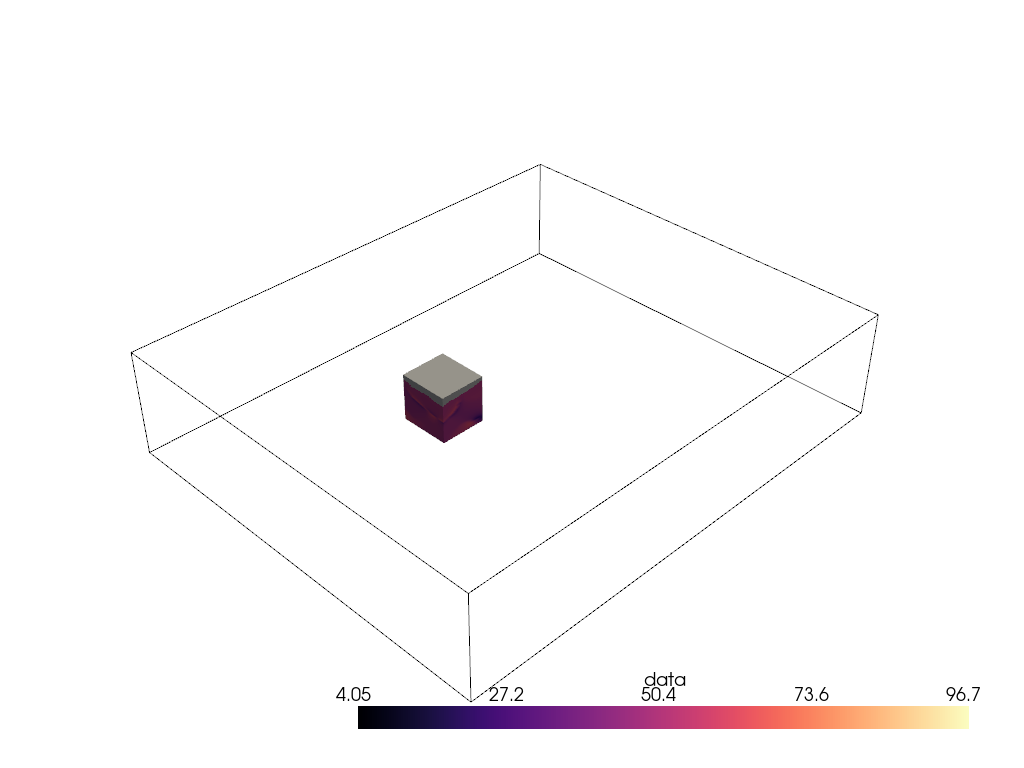
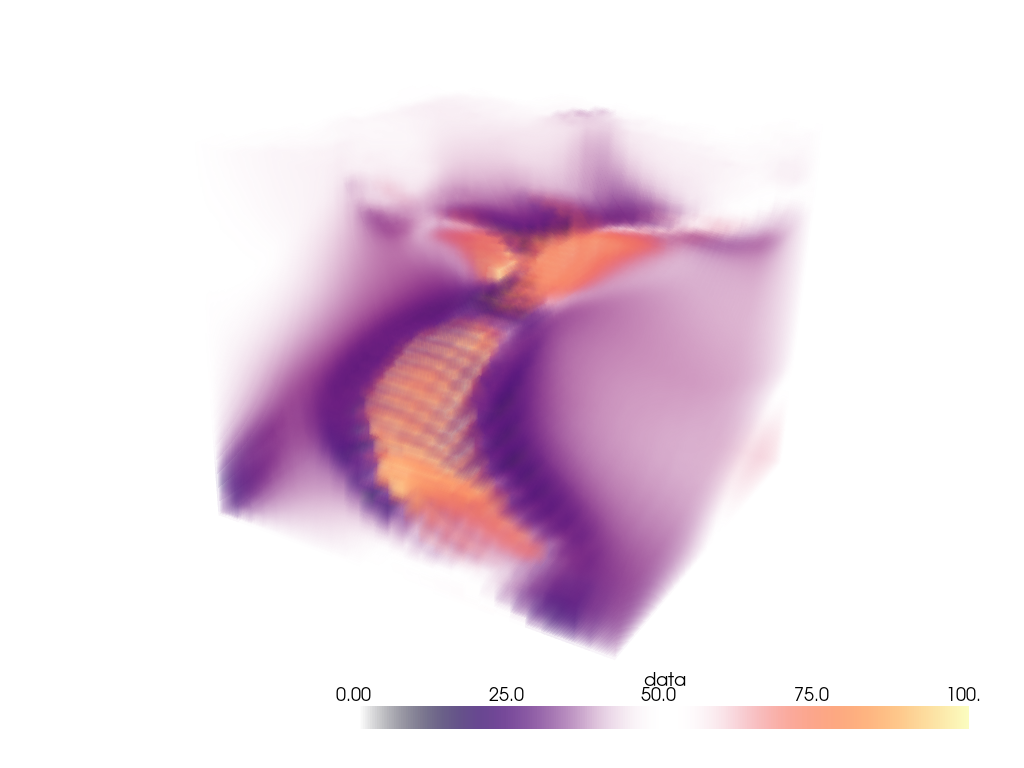
Ah, much better. Let’s now volume render that region of interest.
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_volume(voi, cmap='magma', clim=clim, opacity=opacity, opacity_unit_distance=2000)
pl.camera_position = [
(531554.5542909054, 3944331.800171338, 26563.04809259223),
(599088.1433822059, 3982089.287834022, -11965.14728669936),
(0.3738545892415734, 0.244312810377319, 0.8947312427698892),
]
pl.show()
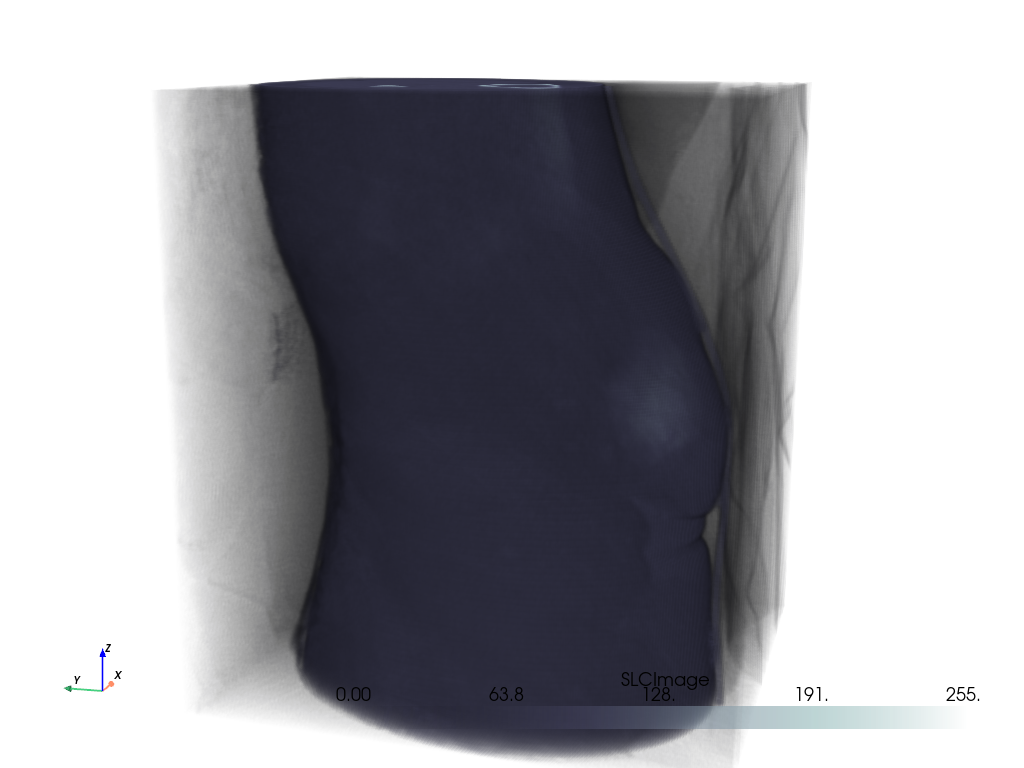
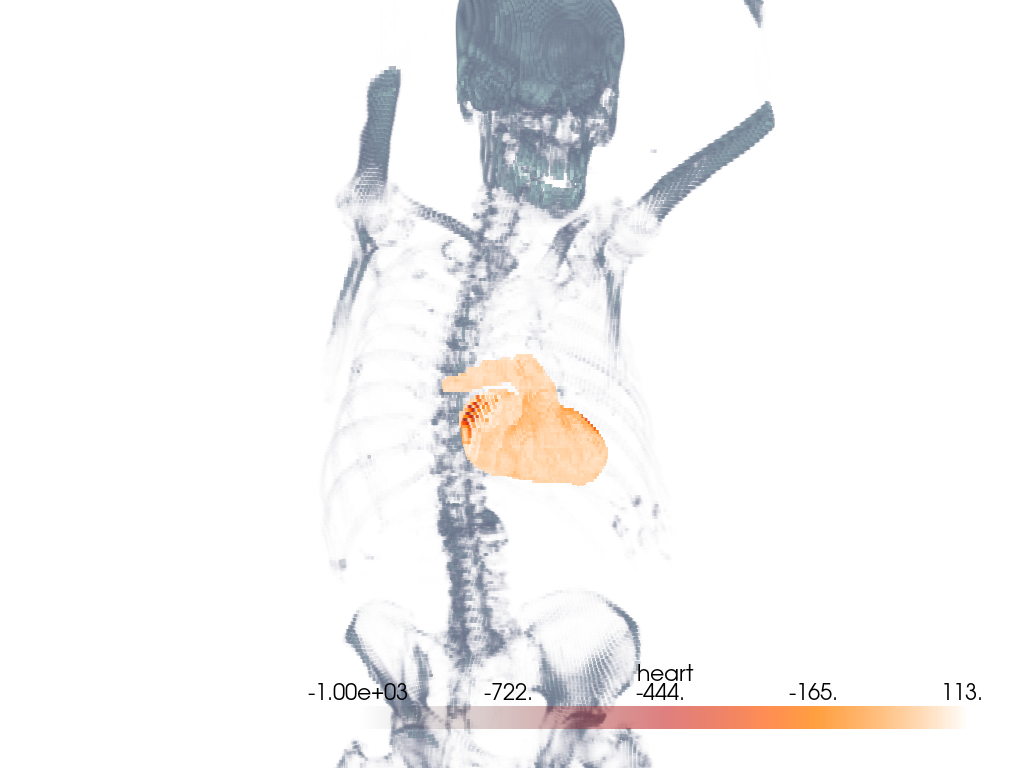
Volume With Segmentation Mask#
Visualize a medical image with a corresponding binary segmentation mask.
For this example, we use download_whole_body_ct_male()
though download_whole_body_ct_female(), or any
other dataset with a corresponding label or mask may be used.
Load the dataset and get the ct image and a mask image. Here, a mask of the heart is used.
dataset = examples.download_whole_body_ct_male()
ct_image = dataset['ct']
heart_mask = dataset['segmentations']['heart']
Use the segmentation mask to isolate the heart in the CT image.
Initialize a new array and image with CT background values. Here, we set the scalar
values to -1000 which typically corresponds to air (low density).
heart_array = np.full_like(ct_image.active_scalars, -1000)
Extract the intensities for the heart segment. We use heart mask’s array to mask the CT image to only extract the intensities of interest.
ct_image_array = ct_image.active_scalars
heart_mask_array = heart_mask.active_scalars
heart_array[heart_mask_array == True] = ct_image_array[heart_mask_array == True] # noqa: E712
Add the masked array to the CT image as a new set of scalar values.
ct_image['heart'] = heart_array
Create the plot.
For the CT image, the opacity is set to a sigmoid function to show the
subject’s skeleton. Since different images have different intensity
distributions, you may need to experiment with different sigmoid functions.
See add_volume() for details.
pl = pv.Plotter()
# Add the CT image.
pl.add_volume(
ct_image,
scalars='NIFTI',
cmap='bone',
opacity='sigmoid_15',
show_scalar_bar=False,
)
# Add masked CT image of the heart and use a contrasting color map.
_ = pl.add_volume(
ct_image,
scalars='heart',
cmap='gist_heat',
opacity='linear',
opacity_unit_distance=np.mean(ct_image.spacing),
)
# Orient the camera to provide a latero-anterior view.
pl.view_yz()
pl.camera.azimuth = 70
pl.camera.up = (0, 0, 1)
pl.camera.zoom(1.5)
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 39.509 seconds)