pyvista.SolidSphereGeneric#
- SolidSphereGeneric(
- radius: VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- theta: VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- phi: VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- center: VectorLike[float] = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
- direction: VectorLike[float] = (0.0, 0.0, 1.0),
- radians: bool = False,
- tol_radius: float = 1e-08,
- tol_angle: float | None = None,
Create a solid sphere with flexible sampling.
A solid sphere fills space in 3D in comparison to
pyvista.Sphere(), which is a 2D surface.This function allows user defined sampling of each spherical coordinate, whereas
pyvista.SolidSphere()only allows linear sampling. Angles are by default specified in degrees.PyVista uses a convention where
thetarepresents the azimuthal angle (similar to degrees longitude on the globe) andphirepresents the polar angle (similar to degrees latitude on the globe). In contrast to latitude on the globe, herephiis 0 degrees at the North Pole and 180 degrees at the South Pole.phi=0is on the positive z-axis by default.theta=0is on the positive x-axis by default.- Parameters:
- radiussequence[
float],optional A monotonically increasing sequence of values specifying radial points. Must have at least two points and be non-negative.
- thetasequence[
float],optional A monotonically increasing sequence of values specifying
thetapoints. Must have at least two points. Can have any value as long as range is within 360 degrees. Large magnitudes may result in problems with endpoint overlap detection.- phisequence[
float],optional A monotonically increasing sequence of values specifying
phipoints. Must have at least two points. Must be between 0 and 180 degrees.- centersequence[
float], default: (0.0, 0.0, 0.0) Center coordinate vector in
[x, y, z].- directionsequence[
float], default: (0.0, 0.0, 1.0) Direction coordinate vector in
[x, y, z]pointing fromcenterto the sphere’s north pole at zero degreesphi.- radiansbool, default:
False Whether to use radians for
thetaandphi. Default is degrees.- tol_radius
float, default: 1.0e-8 Absolute tolerance for endpoint detection for
radius.- tol_angle
float,optional Absolute tolerance for endpoint detection for
phiandtheta. Unit is determined by choice ofradiansparameter. Default is 1.0e-8 degrees or 1.0e-8 degrees converted to radians.
- radiussequence[
- Returns:
pyvista.UnstructuredGridSolid sphere mesh.
See also
pyvista.SolidSphereSphere creation using linear sampling.
pyvista.SphereSphere that describes outer 2D surface.
Examples
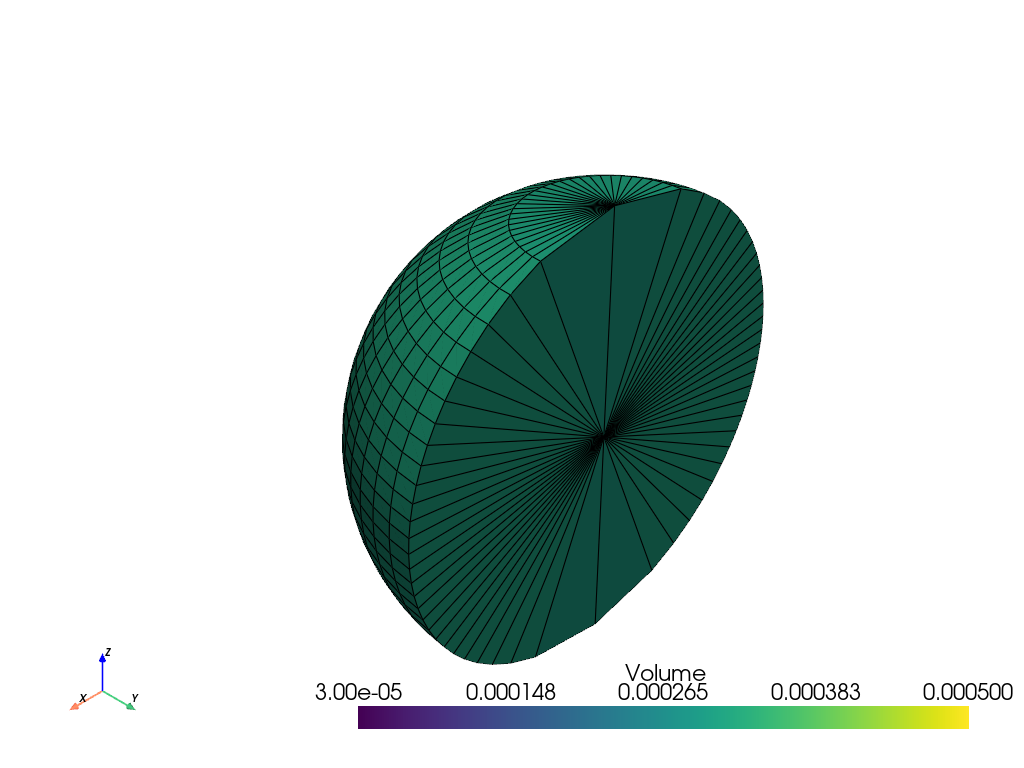
Linearly sampling spherical coordinates does not lead to cells of all the same size at each radial position. Cells near the poles have smaller sizes.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> import numpy as np >>> solid_sphere = pv.SolidSphereGeneric( ... radius=np.linspace(0, 0.5, 2), ... theta=np.linspace(180, 360, 30), ... phi=np.linspace(0, 180, 30), ... ) >>> solid_sphere = solid_sphere.compute_cell_sizes() >>> solid_sphere.plot(scalars='Volume', show_edges=True, clim=[3e-5, 5e-4])
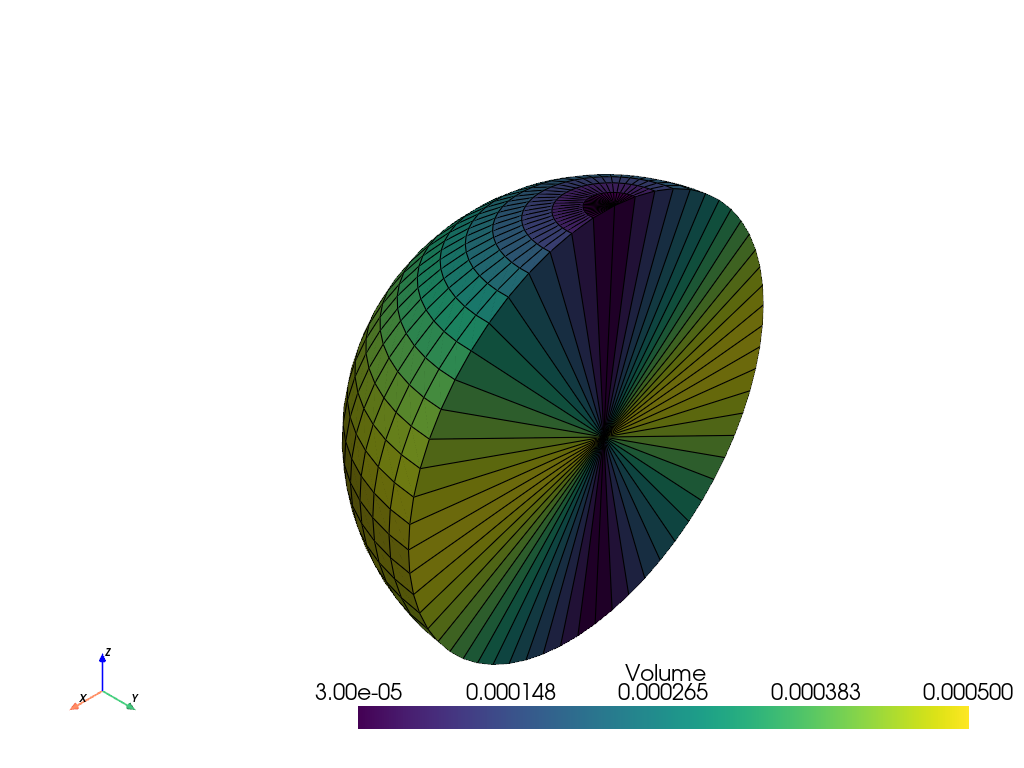
Sampling the polar angle in a nonlinear manner allows for consistent cell volumes. See Sphere Point Picking.
>>> phi = np.rad2deg(np.arccos(np.linspace(1, -1, 30))) >>> solid_sphere = pv.SolidSphereGeneric( ... radius=np.linspace(0, 0.5, 2), ... theta=np.linspace(180, 360, 30), ... phi=phi, ... ) >>> solid_sphere = solid_sphere.compute_cell_sizes() >>> solid_sphere.plot(scalars='Volume', show_edges=True, clim=[3e-5, 5e-4])