Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Marching Cubes#
Generate a surface from a scalar field using the flying edges and
marching cubes filters as provided by the contour filter.
Special thanks to GitHub user stla for providing examples.
from __future__ import annotations
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
Spider Cage#
Use the marching cubes algorithm to extract the isosurface generated from the spider cage function.
a = 0.9
def spider_cage(x, y, z):
x2 = x * x
y2 = y * y
x2_y2 = x2 + y2
return (np.sqrt((x2 - y2) ** 2 / x2_y2 + 3 * (z * np.sin(a)) ** 2) - 3) ** 2 + 6 * (
np.sqrt((x * y) ** 2 / x2_y2 + (z * np.cos(a)) ** 2) - 1.5
) ** 2
# create a uniform grid to sample the function with
n = 100
x_min, y_min, z_min = -5, -5, -3
grid = pv.ImageData(
dimensions=(n, n, n),
spacing=(abs(x_min) / n * 2, abs(y_min) / n * 2, abs(z_min) / n * 2),
origin=(x_min, y_min, z_min),
)
x, y, z = grid.points.T
# sample and plot
values = spider_cage(x, y, z)
mesh = grid.contour([1], values, method='marching_cubes')
dist = np.linalg.norm(mesh.points, axis=1)
mesh.plot(scalars=dist, smooth_shading=True, cmap='plasma', show_scalar_bar=False)
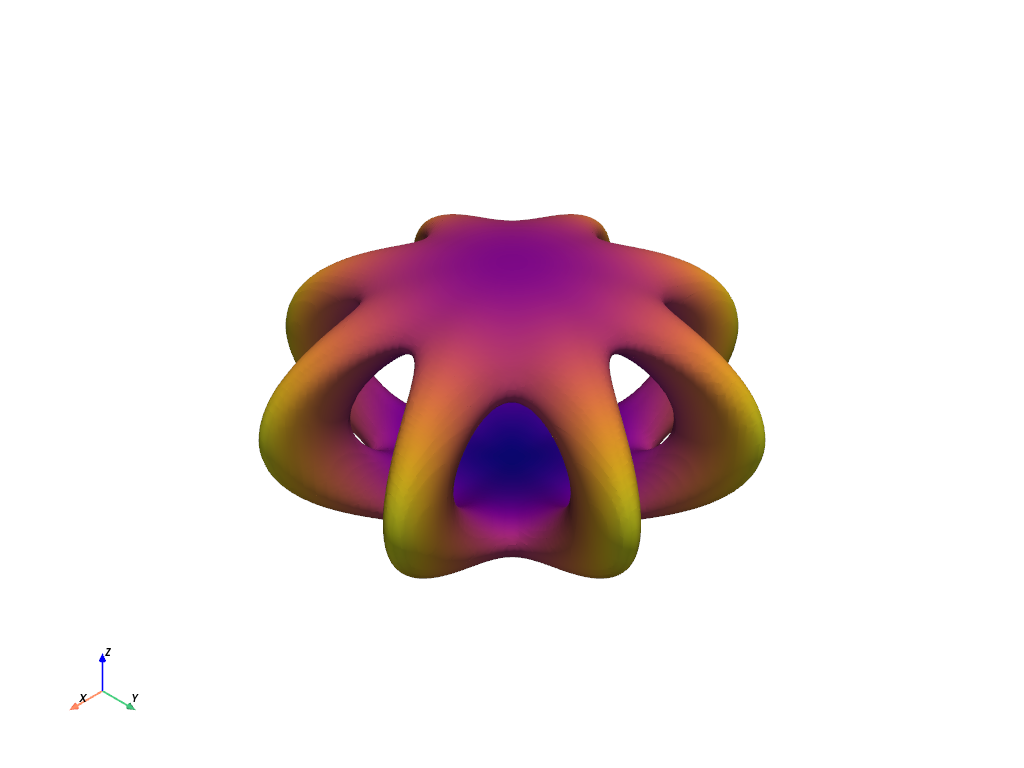
Barth Sextic#
Use the flying edges algorithm to extract the isosurface generated from the Barth sextic function.
phi = (1 + np.sqrt(5)) / 2
phi2 = phi * phi
def barth_sextic(x, y, z):
x2 = x * x
y2 = y * y
z2 = z * z
arr = (
3 * (phi2 * x2 - y2) * (phi2 * y2 - z2) * (phi2 * z2 - x2)
- (1 + 2 * phi) * (x2 + y2 + z2 - 1) ** 2
)
nan_mask = x2 + y2 + z2 > 3.1
arr[nan_mask] = np.nan
return arr
# create a uniform grid to sample the function with
n = 100
k = 2.0
x_min, y_min, z_min = -k, -k, -k
grid = pv.ImageData(
dimensions=(n, n, n),
spacing=(abs(x_min) / n * 2, abs(y_min) / n * 2, abs(z_min) / n * 2),
origin=(x_min, y_min, z_min),
)
x, y, z = grid.points.T
# sample and plot
values = barth_sextic(x, y, z)
mesh = grid.contour([0], values, method='flying_edges')
dist = np.linalg.norm(mesh.points, axis=1)
mesh.plot(scalars=dist, smooth_shading=True, cmap='plasma', show_scalar_bar=False)

Animate Barth Sextic#
Show 20 frames of various isocurves extracted from the Barth sextic function.
def angle_to_range(angle):
return -2 * np.sin(angle)
pl = pv.Plotter(window_size=[800, 800], off_screen=True)
pl.open_gif('barth_sextic.gif')
for angle in np.linspace(0, np.pi, 20, endpoint=False):
# clear the plotter before adding each frame's mesh
pl.clear()
pl.enable_lightkit()
mesh = grid.contour([angle_to_range(angle)], values, method='flying_edges')
dist = np.linalg.norm(mesh.points, axis=1)
pl.add_mesh(
mesh,
scalars=dist,
smooth_shading=True,
rng=[0.5, 1.5],
cmap='plasma',
show_scalar_bar=False,
)
pl.write_frame()
pl.close()
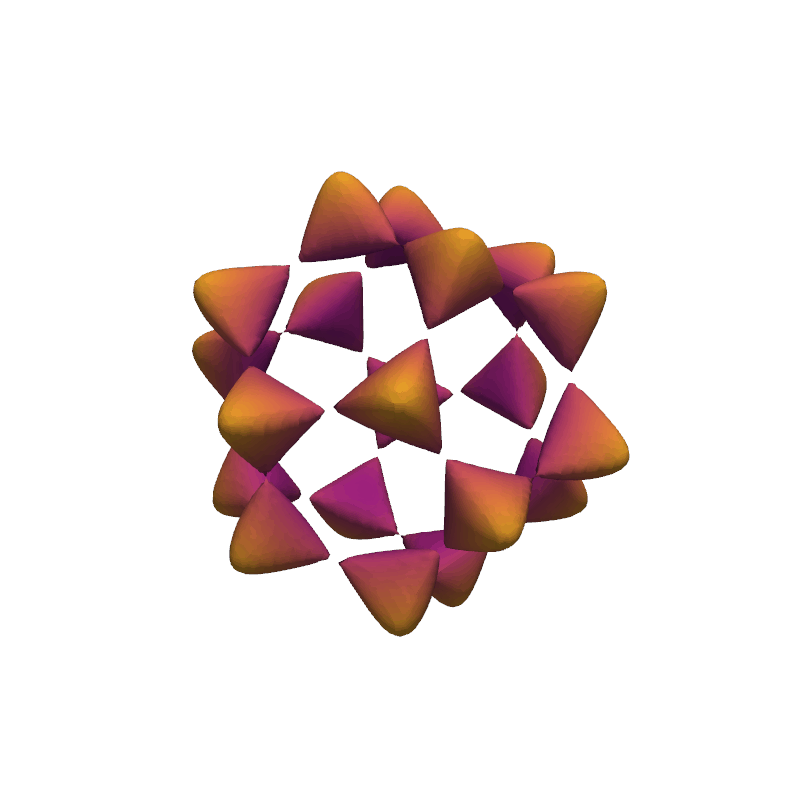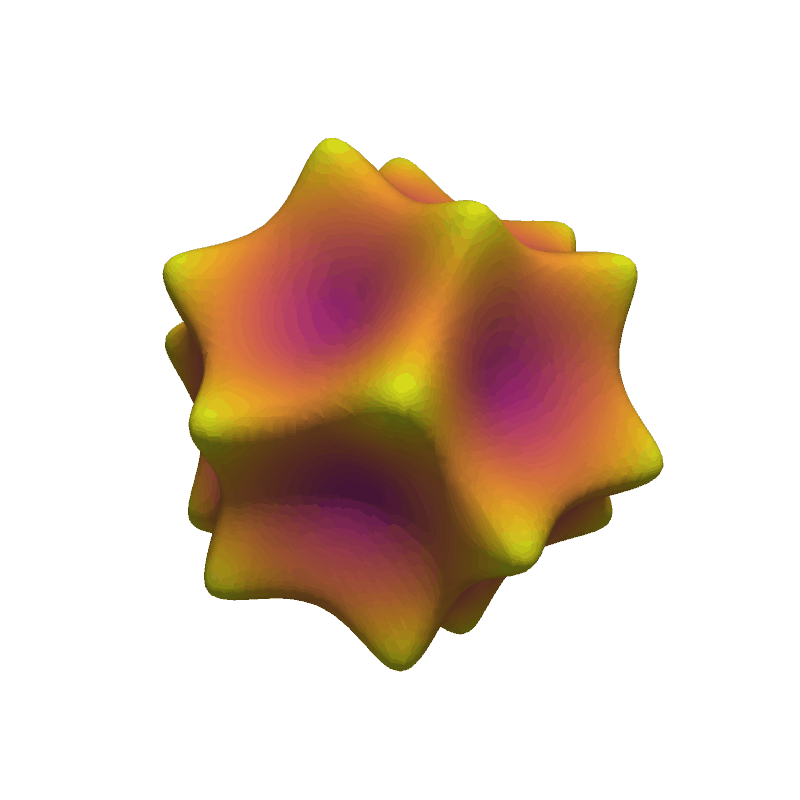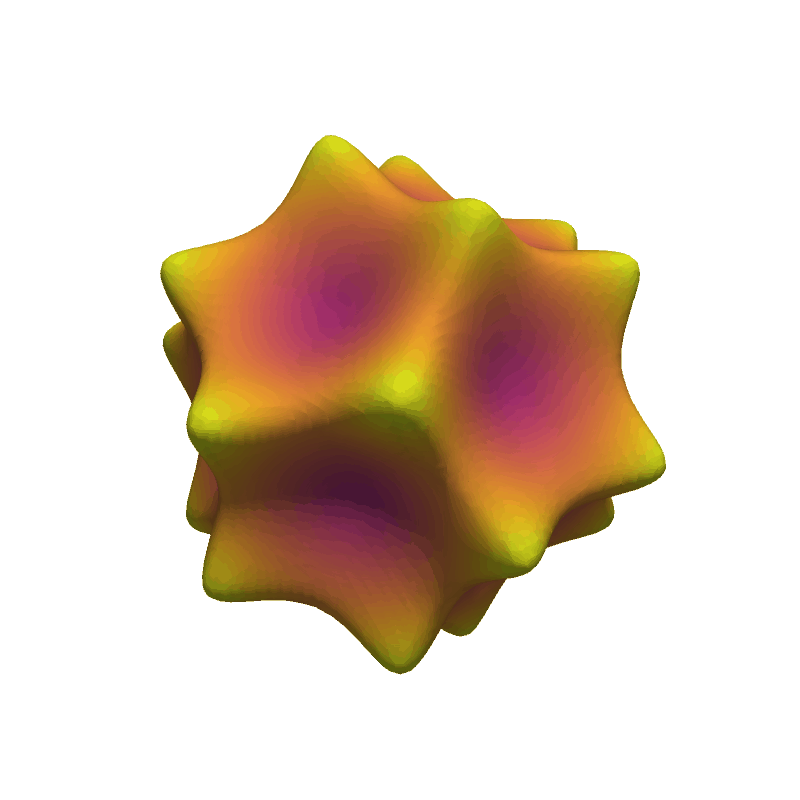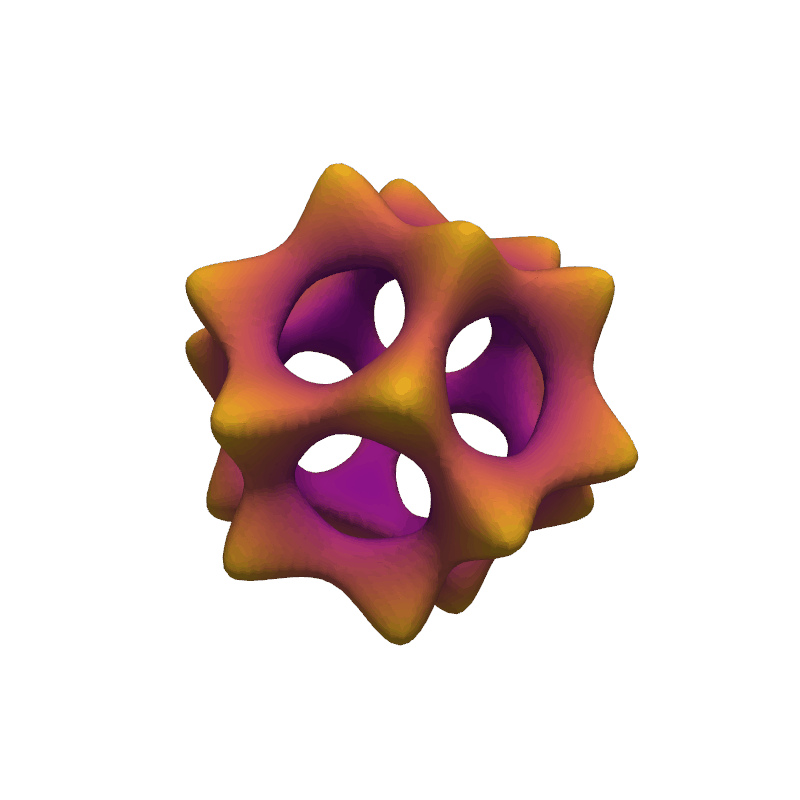
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.948 seconds)