pyvista.PolyDataFilters.boolean_difference#
- PolyDataFilters.boolean_difference(
- other_mesh,
- tolerance=1e-05,
- progress_bar: bool = False,
Perform a boolean difference operation between two meshes.
Essentially, boolean union, difference, and intersection are all the same operation. Just different parts of the objects are kept at the end.
The difference of two manifold meshes
AandBis the volume of the mesh inAnot belonging toB.Note
If your boolean operations don’t react the way you think they should (i.e. the wrong parts disappear), one of your meshes probably has its normals pointing inward. Use
PolyDataFilters.plot_normals()to visualize the normals.Note
Both meshes must be composed of all triangles. Check with
PolyData.is_all_trianglesand convert withPolyDataFilters.triangulate().Changed in version 0.32.0: Behavior changed to match default VTK behavior.
- Parameters:
- other_mesh
pyvista.PolyData Mesh operating on the source mesh.
- tolerance
float, default: 1e-5 Tolerance used to determine when a point’s absolute distance is considered to be zero.
- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- other_mesh
- Returns:
pyvista.PolyDataThe result of the boolean operation.
Examples
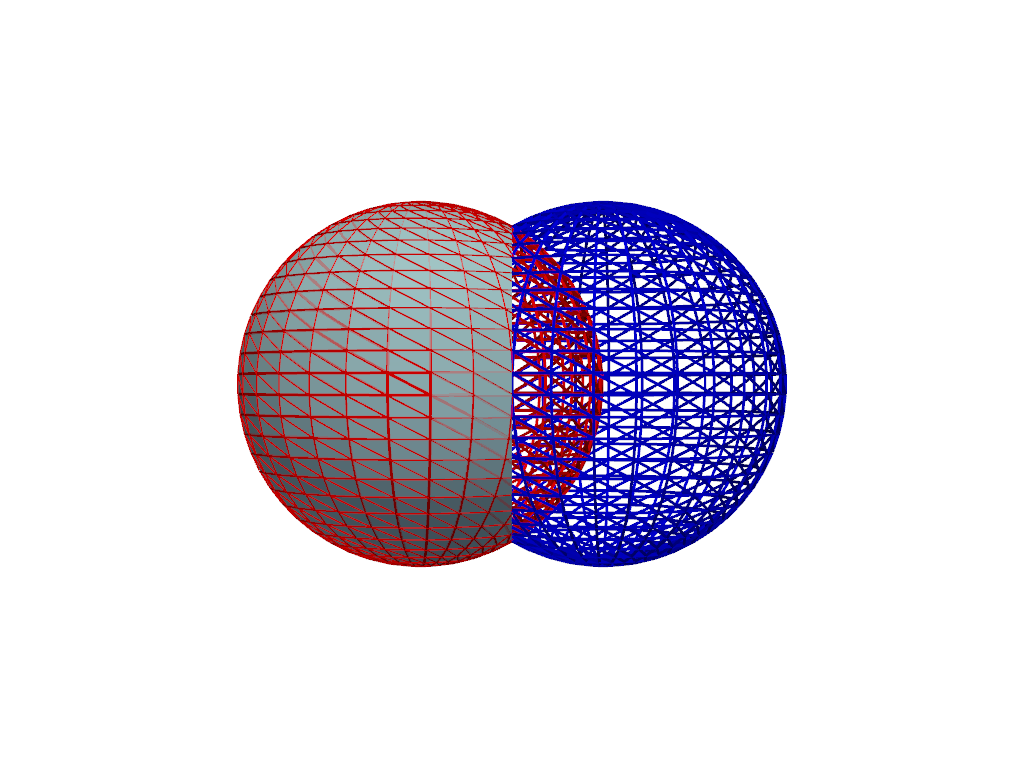
Demonstrate a boolean difference with two spheres. Note how the final mesh only includes
sphere_a.>>> import pyvista as pv >>> sphere_a = pv.Sphere() >>> sphere_b = pv.Sphere(center=(0.5, 0, 0)) >>> result = sphere_a - sphere_b >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(sphere_a, color='r', style='wireframe', line_width=3) >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(sphere_b, color='b', style='wireframe', line_width=3) >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(result, color='lightblue') >>> pl.camera_position = 'xz' >>> pl.show()
See Boolean Operations for more examples using this filter.