pyvista.DataSetFilters.voxelize#
- DataSetFilters.voxelize(
- *,
- reference_volume: ImageData | None = None,
- dimensions: VectorLike[int] | None = None,
- spacing: float | VectorLike[float] | None = None,
- rounding_func: Callable[[VectorLike[float]], VectorLike[int]] | None = None,
- cell_length_percentile: float | None = None,
- cell_length_sample_size: int | None = None,
- progress_bar: bool = False,
Voxelize mesh to UnstructuredGrid.
The voxelization can be controlled in several ways:
Specify the output geometry using a
reference_volume.Specify the
spacingexplicitly.Specify the
dimensionsexplicitly.Specify the
cell_length_percentile. The spacing is estimated from the surface’s cells using the specified percentile.
Use
reference_volumefor full control of the output geometry. For all other options, the geometry is implicitly defined such that the generated mesh fits the bounds of the input mesh.If no inputs are provided,
cell_length_percentile=0.1(10th percentile) is used by default to estimate the spacing.Added in version 0.46.
Note
This method is a wrapper around
voxelize_binary_mask(). See that method for additional information.- Parameters:
- reference_volume
ImageData,optional Volume to use as a reference. The output will have the same
dimensions, andspacingas the reference.- dimensions
VectorLike[int],optional Dimensions of the voxelized mesh. Set this value to control the dimensions explicitly. If unset, the dimensions are defined implicitly through other parameter. See summary and examples for details.
Note
Dimensions is the number of points along each axis, not cells. Set dimensions to
N+1instead forNcells along each axis.- spacing
float|VectorLike[float],optional Approximate spacing to use for the generated mesh. Set this value to control the spacing explicitly. If unset, the spacing is defined implicitly through other parameters. See summary and examples for details.
- rounding_func
Callable[VectorLike[float],VectorLike[int]],optional Control how the dimensions are rounded to integers based on the provided or calculated
spacing. Should accept a length-3 vector containing the dimension values along the three directions and return a length-3 vector.numpy.round()is used by default.Rounding the dimensions implies rounding the actual spacing.
Has no effect if
dimensionsis specified.- cell_length_percentile
float,optional Cell length percentage
pto use for computing the defaultspacing. Default is0.1(10th percentile) and must be between0and1. Thep-th percentile is computed from the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of lengths which are representative of the cell length scales present in the input. The CDF is computed by:Triangulating the input cells.
Sampling a subset of up to
cell_length_sample_sizecells.Computing the distance between two random points in each cell.
Inserting the distance into an ordered set to create the CDF.
Has no effect if
dimensionsis specified.- cell_length_sample_size
int,optional Number of samples to use for the cumulative distribution function (CDF) when using the
cell_length_percentileoption.100 000samples are used by default.- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- reference_volume
- Returns:
UnstructuredGridVoxelized unstructured grid of the original mesh.
See also
voxelize_rectilinearSimilar function that returns a
RectilinearGridwith cell data.voxelize_binary_maskSimilar function that returns a
ImageDatawith point data.
Examples
Create a voxelized mesh with uniform spacing.
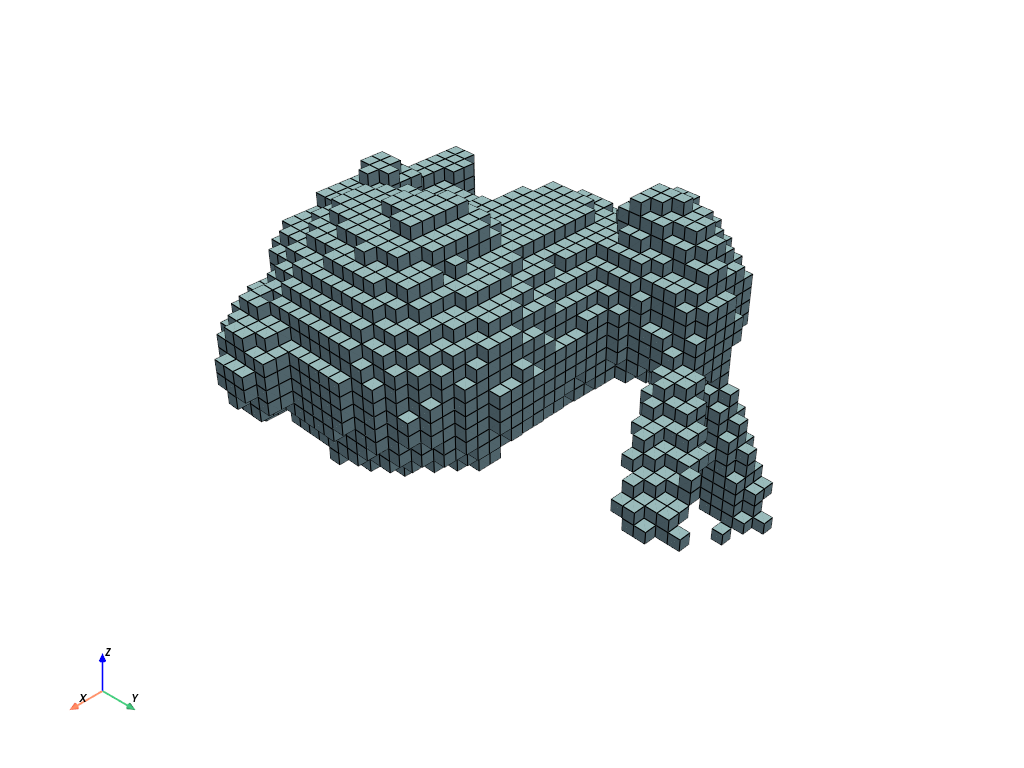
>>> import numpy as np >>> import pyvista as pv >>> from pyvista import examples >>> mesh = examples.download_bunny_coarse() >>> vox = mesh.voxelize(spacing=0.01) >>> vox.plot(show_edges=True)
Create a voxelized mesh using non-uniform spacing.
>>> vox = mesh.voxelize(spacing=(0.01, 0.005, 0.002)) >>> vox.plot(show_edges=True)

The bounds of the voxelized mesh always match the bounds of the input.
>>> mesh.bounds BoundsTuple(x_min = -0.13155962526798248, x_max = 0.18016336858272552, y_min = -0.12048563361167908, y_max = 0.18769524991512299, z_min = -0.14300920069217682, z_max = 0.09850578755140305)
>>> vox.bounds BoundsTuple(x_min = -0.13155962526798248, x_max = 0.18016336858272552, y_min = -0.12048563361167908, y_max = 0.18769524991512299, z_min = -0.14300920069217682, z_max = 0.09650979936122894)
Create a voxelized mesh with
3 x 4 x 5cells. Sincedimensionsis the number of points, not cells, we need to add1to get the number of desired cells.>>> mesh = pv.Box() >>> cell_dimensions = np.array((3, 4, 5)) >>> vox = mesh.voxelize(dimensions=cell_dimensions + 1) >>> vox.plot(show_edges=True)